Quick Start for HVR - PostgreSQL
This quick start guide helps you to get started with HVR for replicating data from an Oracle database to a PostgreSQL database.
To proceed with this replication you must have a basic understanding of HVR's architecture and terminology like Hub, Location, Channel, Location Groups, Actions, etc.
The example here demonstrates how to replicate tables from an Oracle database to the PostgreSQL database.
In real-life scenarios, the source location(s) and the target location(s) reside on different machines and the HVR hub can reside on source or target or a separate machine. However, in this example, for simplicity we have the source, target, and hub databases on the same machine.
Before proceeding with this example ensure that the requirements for using HVR with Oracle and PostgreSQL are met.
For information about access privileges and advanced configuration changes required for performing replication using Oracle and PostgreSQL, see:
Create Demo Schemas and Tables
The initial steps of this demonstration is to create:
- a schema in the source location
- tables in the source schema (and insert values into these tables)
- a schema in the target location
Source Location
Skip this section if you already have a database with tables which you plan to use for this replication.
For this demonstration, create one schema (e.g. sourcedb) with two tables (e.g. dm51_product and dm51_order) in the Oracle source location and insert values into these tables.
Sample SQL statements to create schema and tables in source location
Create Source Schema
create user sourcedb identified by hvr default tablespace users temporary tablespace temp quota unlimited on users;
Create Tables in Source Schema
create table sourcedb.dm51_product ( prod_id number(10) not null, prod_price number(10,2) not null, prod_descrip varchar2(100) not null, primary key (prod_id) );
create table sourcedb.dm51_order ( prod_id number(10) not null, ord_id number(10) not null, cust_name varchar2(100) not null, cust_addr varchar2(100), primary key (prod_id, ord_id) );
Insert Values in Source Tables
insert into sourcedb.dm51_product values (100, 90, 'Book');
insert into sourcedb.dm51_order values (100, 123, 'Customer1', 'P.O. Box 122, Anytown, Anycountry');
Target Location
Create a database (e.g. targetdb):
create database targetdb;
Create user (e.g. hvruser) in the target location.
create user hvruser;
Create schema (e.g. targetdb) for user hvruser in the target location:
create schema targetdb authorization hvruser;
HVR automatically creates tables in target location during HVR Refresh (initial loading) and it is the recommended method for creating tables in the target location. However, if you want to manually create tables in target location, the same can be achieved by executing the required SQL statements.
Sample SQL statements to create tables in target location
create table targetdb.dm51_product ( prod_id integer not null, prod_price decimal(10,2) not null, prod_descrip varchar(100) not null );
create table targetdb.dm51_order ( prod_id integer not null, ord_id integer not null, cust_name varchar(100) not null, cust_addr varchar(100) );
Create Hub Database
The hub database is a database that HVR uses to control its replication activities. The hub database contains HVR catalog tables that hold all specifications of replication such as the names of the replicated databases, the replication direction, and the list of tables to be replicated.
The hub database may be created in one of the supported locations. For this Quick Start Guide, the hub database (e.g. hvrhub) is created in Oracle.
create user hvrhub identified by hvr default tablespace users temporary tablespace temp quota unlimited on users;
Grants/Access Privileges
This section describes the grants/access privileges required for the source schema, target schema, and hub database.
Configure the privileges for the source schema (sourcedb). For more information, see section Grants for Log-Based Capture in Requirements for Oracle.
grant create session to sourcedb; grant create table to sourcedb; grant alter table to sourcedb; grant select any dictionary to sourcedb; grant select any transaction to sourcedb;A user who created the target schema is the owner of the schema and does not require any additional privileges to create and update the tables in it. If the user is not the owner, then configure the privileges for the target schema (targetdb) as follows. For more information, see section Grants for Integrate and Refresh in Requirements for PostgreSQL.
- The User should have permission to read and change replicated tables.
grant select, insert, update, delete on tbl to hvruser
- The User should also have permission to create and drop HVR state tables.
grant create on schema targetdb to hvruser;
- The User should have permission to read and change replicated tables.
Configure the privileges for the hub schema (hvrhub). For more information, see section Grants for Hub Schema in Requirements for Oracle.
grant create session to hvrhub; grant create table to hvrhub; grant create procedure to hvrhub; grant create trigger to hvrhub; grant execute on dbms_alert to hvrhub;
Download and Install HVR
An HVR distribution is available for download at the Fivetran.com website. For more information, see Downloading HVR.
Install HVR on a hub machine. For details on installing HVR, see the respective operating system sections:
The HVR distribution requires a license key in order for the software to operate. Please see the HVR licensing page for more details on how to install the HVR license.
After the installation, you can control HVR using the HVR graphical user interface (HVR GUI).
- If the hub machine is Windows, then HVR GUI can be executed directly on the hub machine.
- To control HVR remotely from your PC, connect to the hub machine using Windows Remote Desktop Connection and launch HVR GUI on the hub machine.
- If the hub machine is Linux, then HVR GUI can be executed directly on the hub machine. However, an application like X Server or VNC viewer must be installed to run HVR GUI directly on Linux.
- To control HVR remotely from your PC, install HVR on the PC (with Windows or macOS) and configure the HVR Remote Listener on the hub machine.
- If the hub machine is Unix, then HVR GUI should typically be run remotely from a PC to control HVR installed on the hub machine. To do this, install HVR on the PC (with Windows or macOS) and configure the HVR Remote Listener on the hub machine.
The HVR Remote Listener allows you to connect HVR GUI available on your PC to the remote HVR hub machine. For more information about connecting to remote HVR installation, see Configuring Remote Installation of HVR on Unix or Linux and Configuring Remote Installation of HVR on Windows.
Launch HVR GUI
This section describes how to launch HVR GUI on various operating systems.
On Windows and macOS, double-click the HVR shortcut icon available on the desktop or execute command hvrgui in the CLI.
On Linux, double-click the hvrgui file available in the HVR_extracted_path/bin directory or execute command hvrgui in the CLI.
Linux requires applications like X server or VNC viewer to execute HVR GUI.
On Unix, HVR GUI is not supported. So, HVR GUI should be run on a remote PC (with Windows, Linux, or macOS) to control HVR installed on the Unix machine.
Register Hub
This section describes how to connect HVR GUI to the hub database.
When you launch HVR GUI for the first time, the Register Hub dialog is displayed automatically. The Register Hub dialog can also be accessed from menu File by selecting Register Hub. Skip steps 1 to 4 if you want to run HVR GUI directly on the hub machine.
Click Connect to HVR on remote machine.
To connect HVR GUI on a PC to a remote HVR hub machine, the HVR Remote Listener must be configured and running on the HVR hub machine.
Enter the name or IP address of the hub machine in the Node field (e.g. myserver).
Enter the port number (defined in the HVR Remote Listener of the hub machine) in the Port field (e.g. 4343).
Enter the Login (e.g. myserveradmin) and Password for the hub machine. By default, this is the operating system login credentials of the hub machine.
Select Oracle in the Class pane.
Specify Database Connection details.
- Enter the directory path in ORACLE_HOME. You can also click the browse button to select the directory path.
- Enter the Oracle System ID in ORACLE_SID or TNS credentials.
- Enter the user name of the hub database in User (e.g. hvrhub).
- Enter the password for the hub database in Password (e.g. hvr).
Click Connect.

Click Yes in the prompt dialog asking to create catalog tables in the hub database.
HVR displays this prompt when connecting to a hub database for the first time.
On connecting successfully to the hub database, the navigation tree pane displays the hub machine and the hub database. Location Configuration, Channel Definitions, and Scheduler are displayed under the hub database.
Create Locations
This section describes how to create locations in HVR GUI. A location is a storage place (for example, a database or file storage) from/into where HVR captures (source location) or integrates (target location) changes.
Create a source location (e.g. src) connected to the source schema (sourcedb) in Oracle.
- In the navigation tree pane, right-click Location Configuration ▶ New Location.
- Enter the Location name and Description for the location.
- Select Oracle in the Class pane.
- Specify the Database Connection details. For more information on the Database Connection fields, see section Location Connection in Requirements for Oracle.
Enter the directory path for ORACLE_HOME. You can also click browse to select the directory path.
Enter the Oracle System ID in ORACLE_SID or TNS credentials or RAC credentials.
For RAC connectivity, ensure to provide the remote machine connection details under the Connection tab.
Enter username sourcedb of the source schema in User.
Enter the password for the source schema in Password.
- Click Test Connection to verify the connection to the source database.
- Click OK.
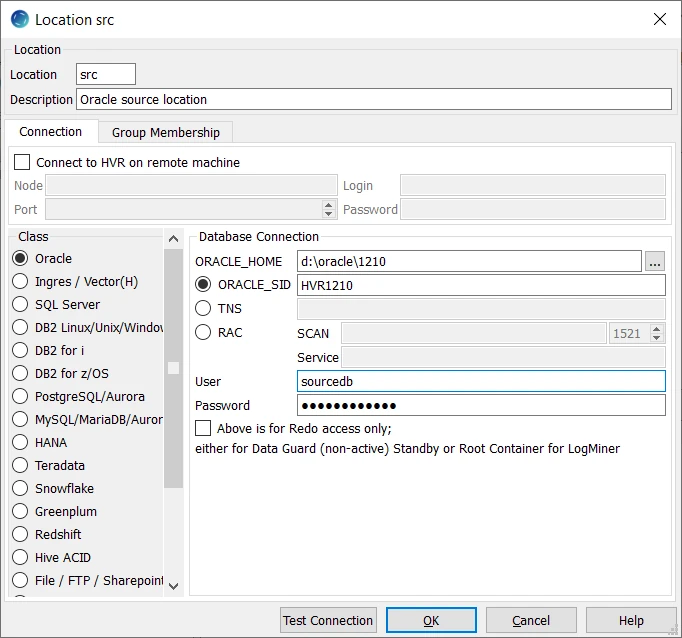
Create a target location (e.g. tgt) connected to the target PostgreSQL database (targetdb).
- In the navigation tree pane, right-click Location Configuration ▶ New Location.
- Enter the Location name and Description for the location.
- Select PostgreSQL in the Class pane.
- Specify the Database Connection details. For more information on the Database Connection fields, see section Location Connection in Requirements for PostgreSQL.
Enter the directory path for PostgreSQL Client in PGLIB. You can also click browse to select the directory path.
Enter the hostname or IP-address of the machine on which the PostgreSQL server is running in Node.
Enter the port on which the PostgreSQL server is expecting connections in Port.
Enter the name of the PostgreSQL database in Database, e.g. targetdb.
Enter the username to connect HVR to the PostgreSQL database in User, e.g. hvruser.
Enter the password of the User to connect HVR to the PostgreSQL database in Password.
- Click Test Connection to verify the connection to location database.
- Click OK.
Create Channel
This section describes how to create a channel (e.g. hvrdemo) in HVR.
In the navigation tree pane, right-click Channel Definitions ▶ New Channel.
Enter the Channel name and Description for the channel in the New Channel dialog.
Click OK.
Create Location Groups
This section describes how to create location groups in the channel. The location groups are used for defining actions on the location. Typically, a channel contains two location groups - one for the source location and one for the target location. Each location group can contain multiple locations.
In this example, create one source location group (e.g. SRCGRP) and one target location group (e.g. TGTGRP).
- In the navigation tree pane, click + next to the channel (hvrdemo).
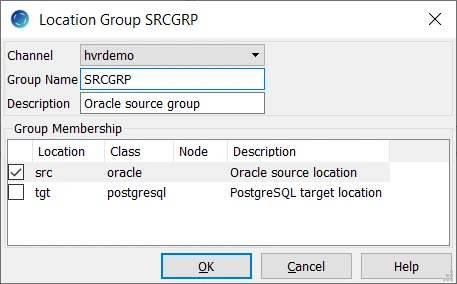
- Create the source location group (SRCGRP):
- Right-click Location Groups ▶ New Group.
- Enter the Group Name and Description for the source location group.
- Select the source location (src) in Group Membership and click OK.
- Create the target location group (TGTGRP):
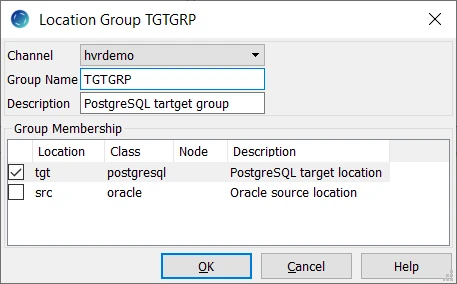
- Right-click Location Groups ▶ New Group.
- Enter the Group Name and Description for the target location group.
- Select the target location (tgt) from Group Membership and click OK.
Define Actions
This section describes how to define actions on the location groups (SRCGRP and TGTGRP). Actions define the behavior of a replication activity.
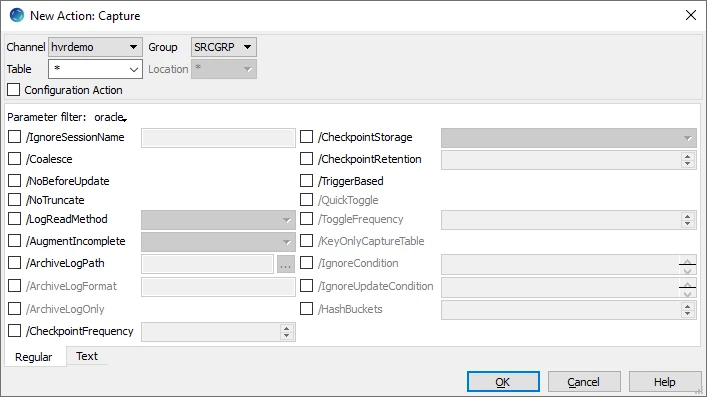
- Define action Capture to capture changes from all tables in the source location group.
- In the navigation tree pane, right-click source location group SRCGRP ▶ New Action ▶ Capture.
- Click OK.
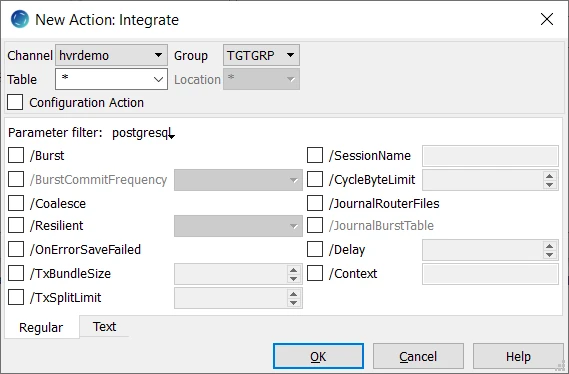
- Define action Integrate to integrate changes into the tables of the target location group.
- In the navigation tree pane, right-click target location group TGTGRP ▶ New Action ▶ Integrate.
- Click OK.
Select Table(s)
This section describes how to select the tables (dm51_order and dm51_product) from the source location for replication. The Table Explore dialog allows you to select schema(s) and/or table(s) for replication.
- In the navigation tree pane, right-click Tables ▶ Table Explore.
- Select source location (src) from the list.
- Click Connect.
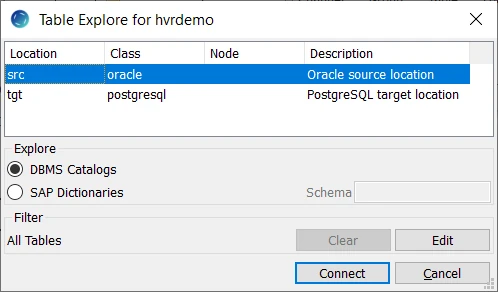
- Select tables from the Table Explore dialog. Use the Shift or Ctrl key to select multiple tables or Ctrl+A to select all tables.
- Click Add to add the selected tables to the channel.
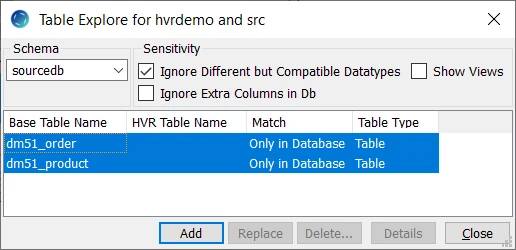
- Click OK in HVR Table Name dialog.
- Click Close in Table Explore dialog.
Initialize
This section describes how to initialize the replication. HVR Initialize first checks the channel and creates the replication jobs in the HVR Scheduler.
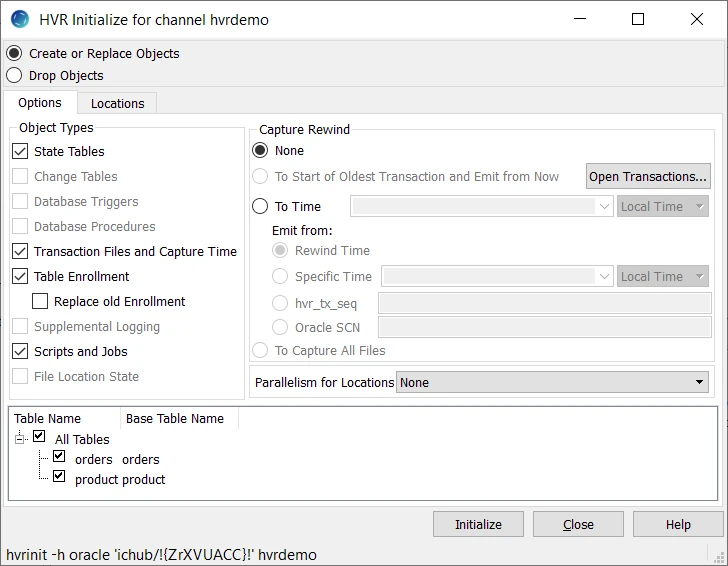
In the navigation tree pane, right-click channel hvrdemo ▶ HVR Initialize.
Ensure that Create or Replace Objects, the corresponding options, and tables are selected as shown in the HVR Initialize dialog below.
Click Initialize.
Click OK. The prompt dialog informs you of the replications jobs created.
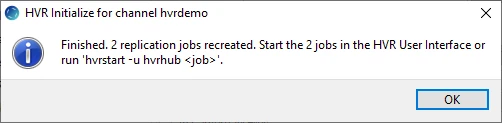
Click Close in the HVR Initialize dialog.
Click the Scheduler node in the navigation tree pane to display the capture and integrate jobs in the Jobs pane.
For more information about initiating replication in HVR, see section Replication Overview.
Start Scheduler
This section describes how to start the HVR Scheduler. The HVR Scheduler is a process which runs jobs defined in the catalog table HVR_JOB. This catalog table can be found in the hub database. On Unix or Linux, the HVR Scheduler runs as a daemon. On Windows, the HVR Scheduler runs as a system service.
- In the navigation tree pane, right-click Scheduler ▶ Start.
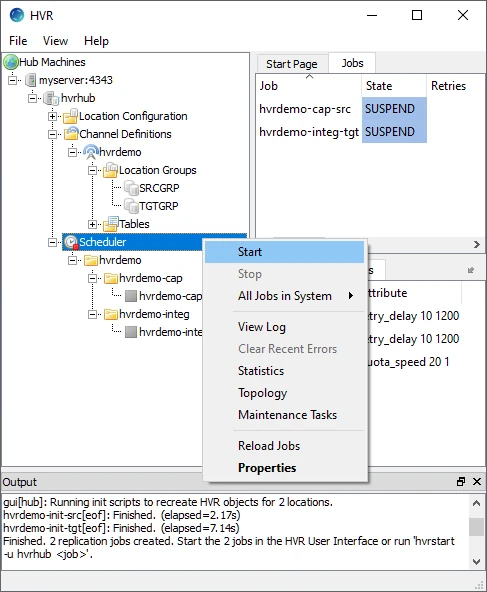
- On Windows, the following steps are required to create the HVR Scheduler system service.
- Click Create... in the prompt asking to create the service hvrscheduler_hvrhub.
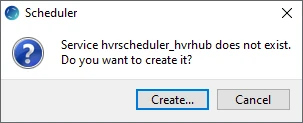
- In the Create Windows Service dialog, select Local System Account ('SYSTEM') and click Create.
- Click Create... in the prompt asking to create the service hvrscheduler_hvrhub.
Start Capture Job
This section describes how to start the job for capturing changes from the source location (src). By starting the Capture job in HVR Scheduler, HVR begins capturing all changes since the moment HVR Initialize was executed. This 'capture begin moment' can be modified using option Capture Rewind available on the Advanced Options tab of the HVR Initialize dialog.
In the navigation tree pane, click Scheduler.
Start the capture job. In the Jobs pane, right-click capture job hvrdemo-cap-src ▶ Start.
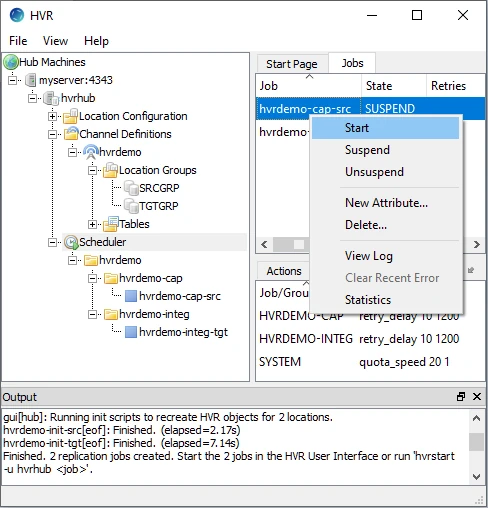
Click Yes in the Start dialog.
On starting the capture job (hvrdemo-cap-src) successfully, the status of the job changes from SUSPEND to RUNNING.
Refresh
This section describes how to perform initial load into the target database. HVR Refresh copies all existing data from the source location (src) to the target location (tgt) and optionally creates new tables and keys in the target location.
- In the navigation tree pane, right-click channel hvrdemo ▶ HVR Refresh.
- Select the table(s) that needs to be copied from the source location to the target location.
- Select Create Absent Tables in HVR Refresh dialog.
- Click Refresh.
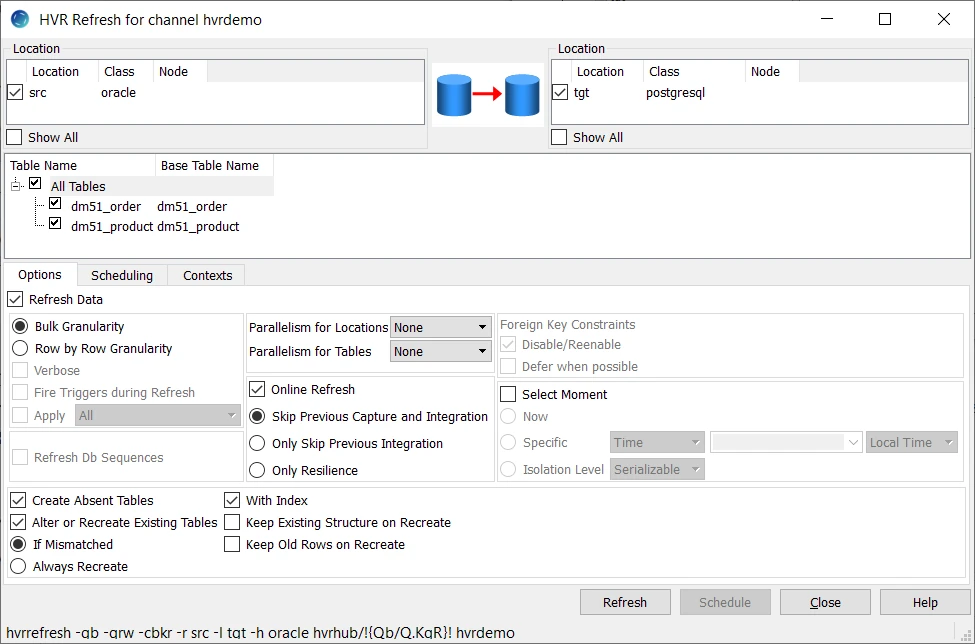
- Click Yes to begin HVR Refresh. When the refresh is completed, the Refresh Result dialog displays the total number of rows replicated from the selected tables.
- Click Close in the Refresh Result dialog and then in the HVR Refresh dialog.
Start Integrate Job
This section describes how to start the job to integrate changes into the target location (tgt).
In the navigation tree pane, click Scheduler.
Start the integrate job. In the Jobs pane, right-click integrate job hvrdemo-integ-tgt ▶ Start.
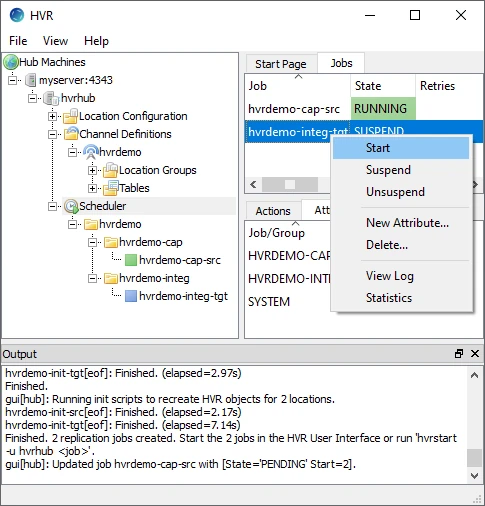
Click Yes in the Start dialog.
On starting the integrate job (hvr_demo-integ-tgt) successfully, the status of the job changes from SUSPEND to RUNNING.
Verify Replication
This section describes two methods for verifying the HVR's replication activity.
Viewing Log File
HVR creates separate log files for the hub, channel (hvrdemo), and for each replication job (hvrdemo-cap-src and hvrdemo-integ-tgt). These log files contain the details of the changes captured and integrated.
Replication can be verified by inspecting the channel log file.
To view the replication activity log:
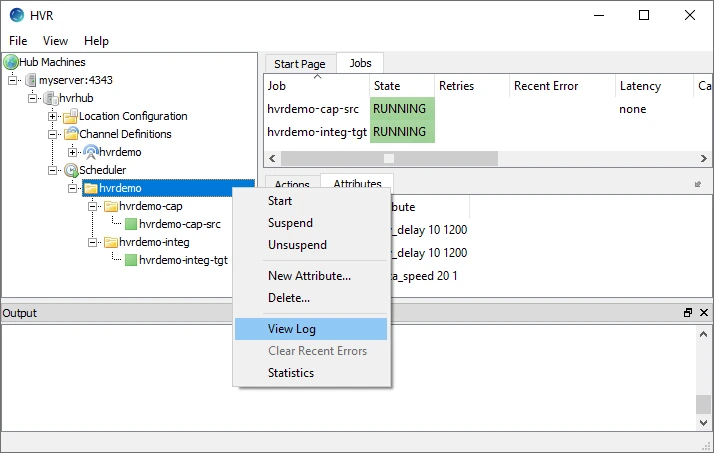
In the navigation tree pane, click + next to the Scheduler.
Right-click hvrdemo ▶ View Log to view the log of both capture and integrate jobs.
The logs for both capture and integrate jobs are displayed in the logs pane (Log of channel hvrdemo) at the bottom of the screen.
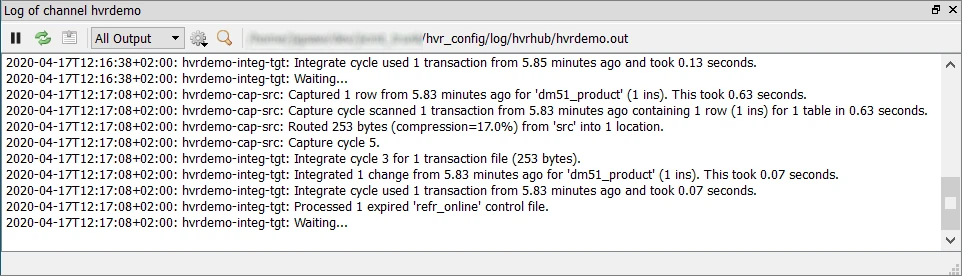
The directory path for the HVR log files is displayed in the log tab.
Right-clicking a particular job and selecting View Log displays logs related to that job alone.
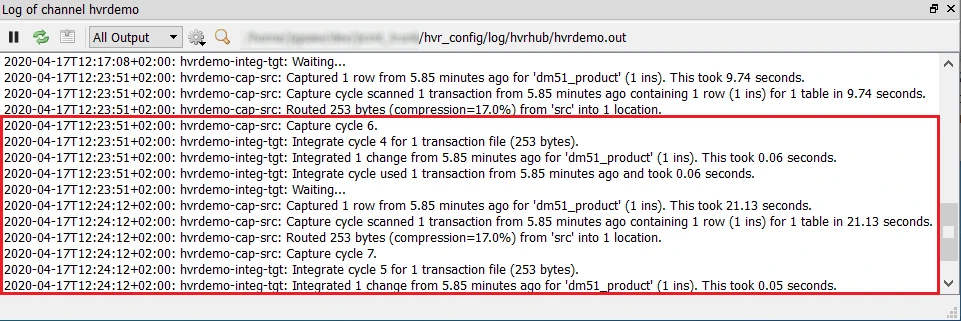
Insert, update, or delete value(s) in the source location schema. For example:
insert into sourcedb.dm51_product values (101, 91, 'Pencil');The output log is updated and indicates that the change is captured from the source location and integrated into the target location:
Using HVR Compare
HVR Compare allows you to verify the replication activity by comparing the data in source and target locations.
To compare the source and target locations:
Suspend the integrate job (hvrdemo-integ-tgt):
- In the navigation tree pane, click Scheduler.
- In the Jobs pane, right-click integrate job hvrdemo-integ-tgt ▶ Suspend.
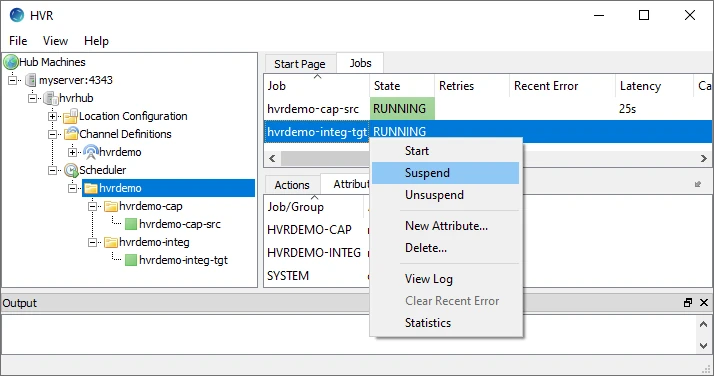
- Click Yes in the Suspend dialog.
Insert, update, or delete value(s) in the source location schema. For example:
insert into sourcedb.dm51_product values (101, 91, 'Pencil');Execute HVR Compare:
In the navigation tree pane, right-click channel hvrdemo ▶ HVR Compare.
Select the source location (src) on the left side and the target location (tgt) on the right side.
Select Generate Compare Event in the Scheduling tab.
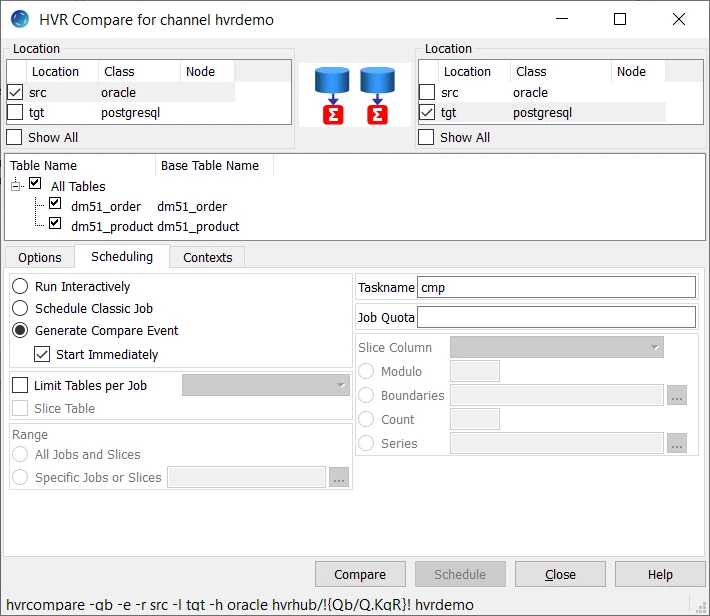
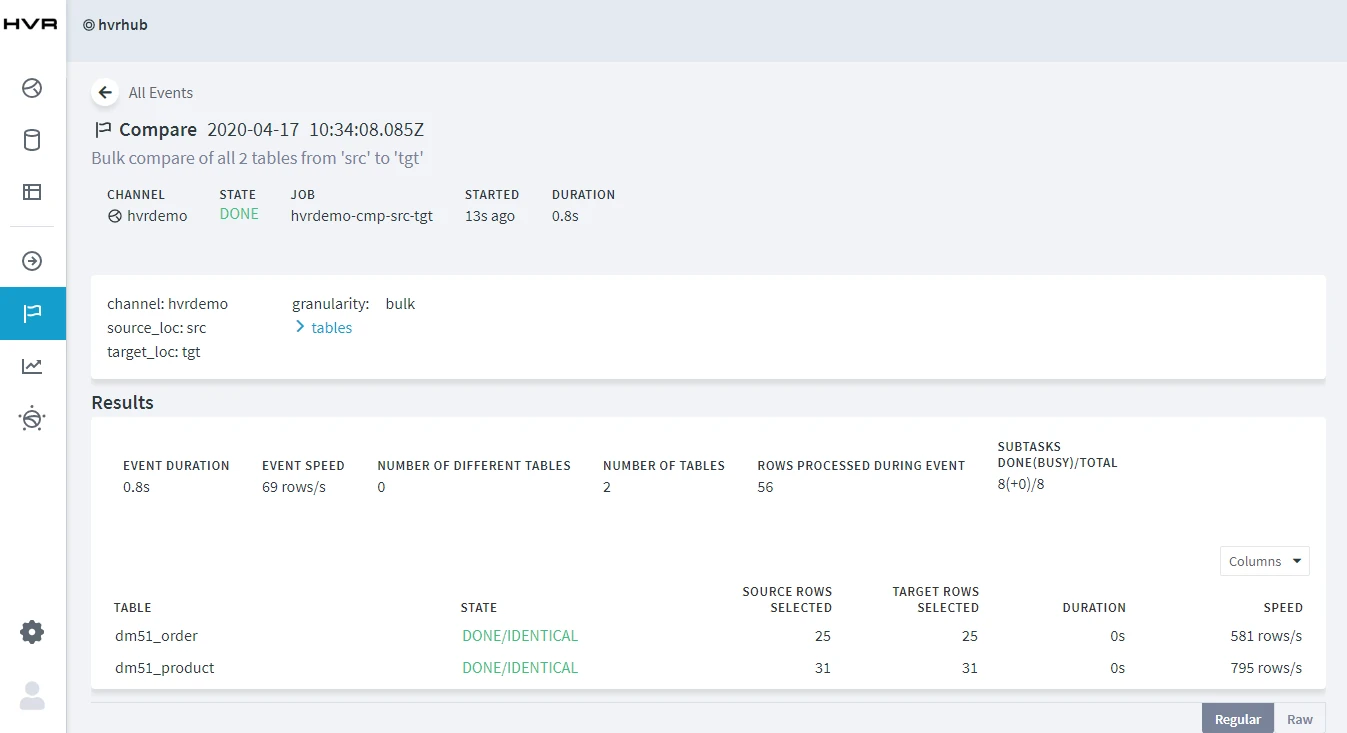
Click Compare.
On completion, the compare result is displayed in the HVR web app. If the State column displays DONE/DIFFERENT, it indicates the data in the source and target locations are not identical.
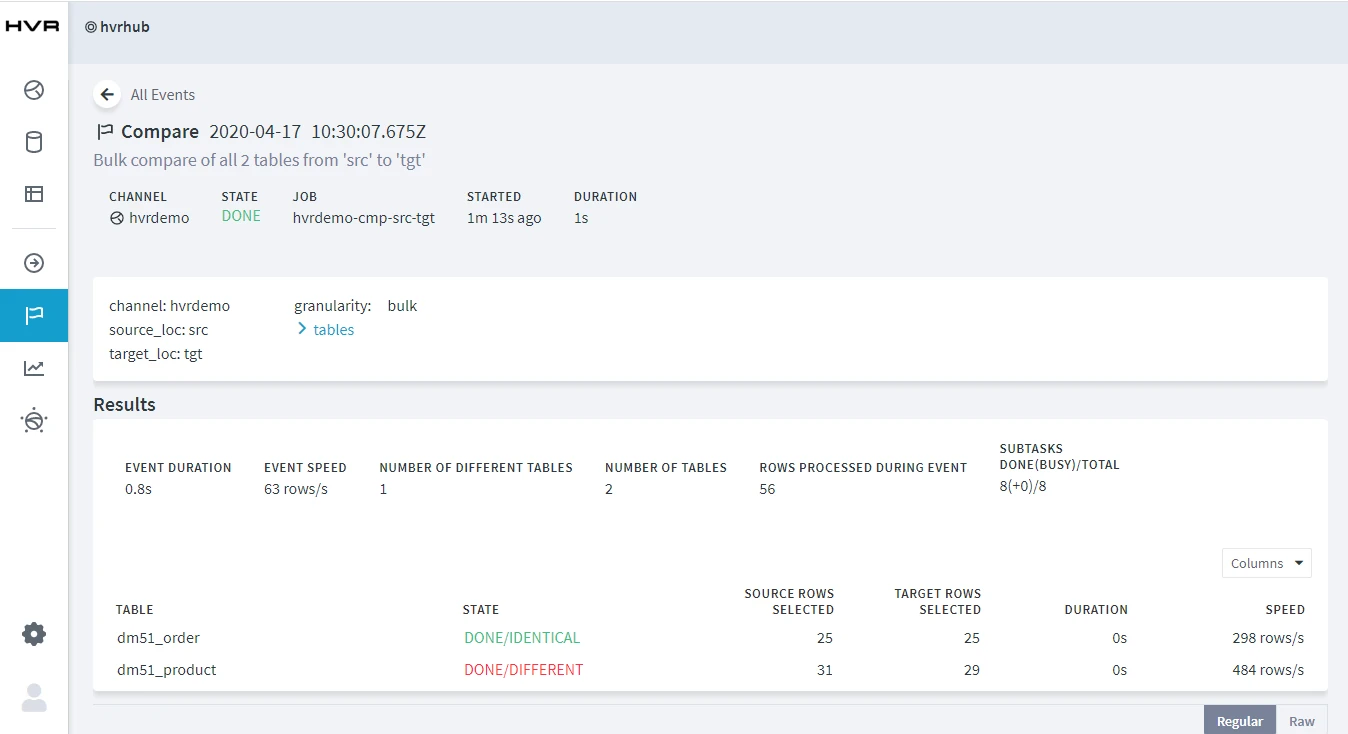
Start Integrate Job (hvrdemo-integ-tgt), the changes made in source location (in step 2) will be integrated to the target location now.
Execute HVR Compare again (step 3). In the compare result screen, if the State column displays DONE/IDENTICAL, it indicates the changes are replicated successfully.