Quick Start for HVR - Ingres
This quick start guide helps you to get started with HVR for replicating data between Ingres databases.
To proceed with this replication you must have basic understanding about HVR's architecture and terminologies like Hub, Location, Channel, Location Groups, Actions etc.
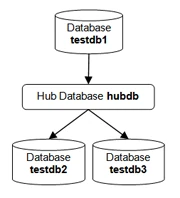
The example here demonstrates how to replicate tables from one Ingres database (source location) to another two Ingres databases (target location).
In real-life scenarios, the source location(s) and the target location(s) reside on different machines and the HVR hub can reside on source or target or a separate machine. However, in this example, for simplicity we have the source, target, and HVR hub database on the same machine.
Before proceeding with this example ensure that the requirements for using HVR with Ingres are met.
For information about access privileges and advanced configuration changes required for performing replication using Ingres, see Requirements for Ingres and Vector.
Create Test Databases and Tables
Create three test databases, each containing two empty tables named dm01_product and dm01_order. If replication is configured between existing databases and tables then this step should be skipped.
$ createdb testdb1 $ createdb testdb2 $ createdb testdb3 $ cd $HVR_HOME/demo/hvr_demo01/base/ingres $ sql testdb1 < hvr_demo01.cre $ sql testdb1 < hvr_demo01.mod $ sql testdb2 < hvr_demo01.cre $ sql testdb2 < hvr_demo01.mod $ sql testdb3 < hvr_demo01.cre $ sql testdb3 < hvr_demo01.mod $ ckpdb +j testdb1
The last command (to checkpoint the source database) is needed so that if HVR log–based capture cannot find a change anymore in the Ingres log file it can always look into the Ingres journal files.
Create the Hub Database
Create the hub database, in which the HVR GUI will store the channel definition.
$ createdb hvrhub
Download and Install HVR
An HVR distribution is available for download at the Fivetran.com website. For more information, see Downloading HVR.
Install HVR on a hub machine. For details on installing HVR, see the respective operating system sections:
The HVR distribution requires a license key in order for the software to operate. Please see the HVR licensing page for more details on how to install the HVR license.
After the installation, you can control HVR using the HVR graphical user interface (HVR GUI).
- If the hub machine is Windows, then HVR GUI can be executed directly on the hub machine.
- To control HVR remotely from your PC, connect to the hub machine using Windows Remote Desktop Connection and launch HVR GUI on the hub machine.
- If the hub machine is Linux, then HVR GUI can be executed directly on the hub machine. However, an application like X Server or VNC viewer must be installed to run HVR GUI directly on Linux.
- To control HVR remotely from your PC, install HVR on the PC (with Windows or macOS) and configure the HVR Remote Listener on the hub machine.
- If the hub machine is Unix, then HVR GUI should typically be run remotely from a PC to control HVR installed on the hub machine. To do this, install HVR on the PC (with Windows or macOS) and configure the HVR Remote Listener on the hub machine.
The HVR Remote Listener allows you to connect HVR GUI available on your PC to the remote HVR hub machine. For more information about connecting to remote HVR installation, see Configuring Remote Installation of HVR on Unix or Linux and Configuring Remote Installation of HVR on Windows.
Launch HVR GUI
This section describes how to launch HVR GUI on various operating systems.
On Windows and macOS, double-click the HVR shortcut icon available on the desktop or execute command hvrgui in the CLI.
On Linux, double-click the hvrgui file available in the HVR_extracted_path/bin directory or execute command hvrgui in the CLI.
Linux requires applications like X server or VNC viewer to execute HVR GUI.
On Unix, HVR GUI is not supported. So, HVR GUI should be run on a remote PC (with Windows, Linux, or macOS) to control HVR installed on the Unix machine.
Register Hub
This section describes how to connect HVR GUI to the hub database.
- First, register the hub database: right-click on hub machines▶ Register hub.
- Enter connection details.
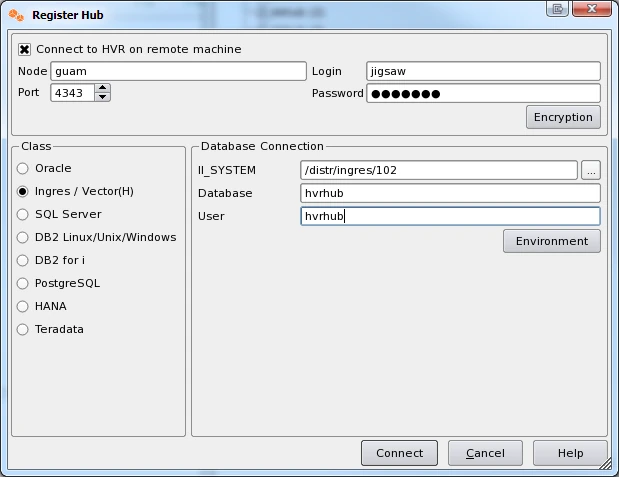
In this example the hub is a machine called guam, where an INET daemon is listening on port 4343. See section Installing HVR on Unix or Linux for how to configure this.
For a new hub database a dialog will prompt Do you wish to create the catalogs?; answer Yes.
Create Locations
Next create three locations (one for each test database) using right-click on Location Configuration ▶ New Location.
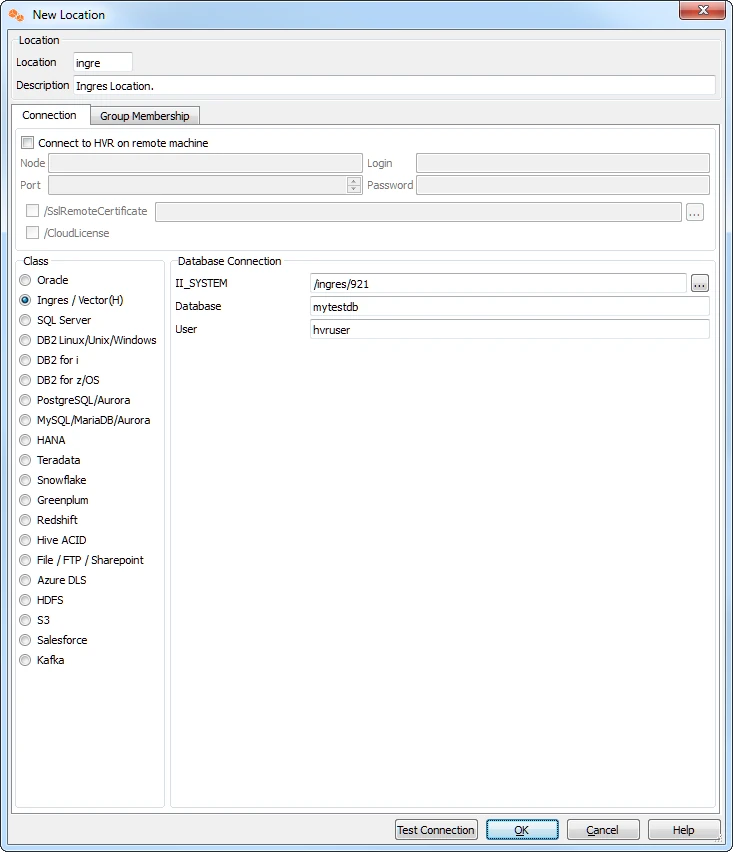
In this example there is no need to check Connect to HVR on remote machine because testdb1 is on the same machine as the hub.
Ignore the Group Membership tab for now.
Make locations for testdb2 and testdb3 too.
Now define a channel using Channel Definitions ▶ New Channel.
Create Location Groups
The channel needs two location groups. Under the new channel, right-click Location Groups ▶ New Group. Enter a group name (for instance CENTRAL).
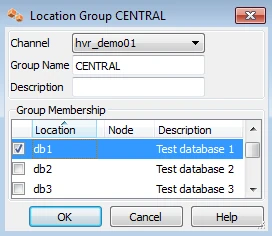
Add location db1 as a member of this group by checking the box for db1.
Then create a second location group, called DECENTRAL that has members db2 and db3.
The new channel also needs a list of tables to replicate. This can be done as follows: right-click Tables ▶ Table Explore.
- Choose the first of the three locations ▶ Connect.
- In the Table Explore window, click on both tables and click Add.
- In new dialog HVR Table Name click OK.
- Close the Table Explore window.
- Perform table select again on one of the other locations and confirm that all tables to be replicated have value Same in column Match.
Define Actions
The new channel needs two actions to indicate the direction of replication.
Right-click group CENTRAL ▶ New Action ▶ Capture.
Right-click Group DECENTRAL ▶ New Action ▶ Integrate. Check /OnErrorSaveFailed, this affects how replication errors are handled.
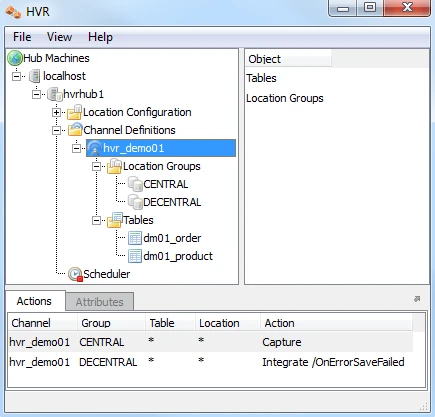
Note that the Actions pane only displays actions related to the objects selected in the left-hand pane. So click channel hvr_demo01 to see both actions.
Initialize
Now that the channel definition is complete, create the runtime replication system.
- Right-click channel hvr_demo01 ▶ HVR Initialize.
- Choose Create or Replace Objects and click HVR Initialize.
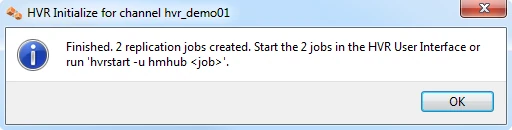
From the moment that HVR Initialize is done, all changes to database sourcedb will be captured by HVR when its capture job looks inside the logging.
HVR initialize also creates three replication jobs, which can be seen under the Scheduler node in the GUI.
Start Scheduling of Replication Jobs
Start the Scheduler on the hub machine by clicking in the HVR GUI on the Scheduler node of the hub database.
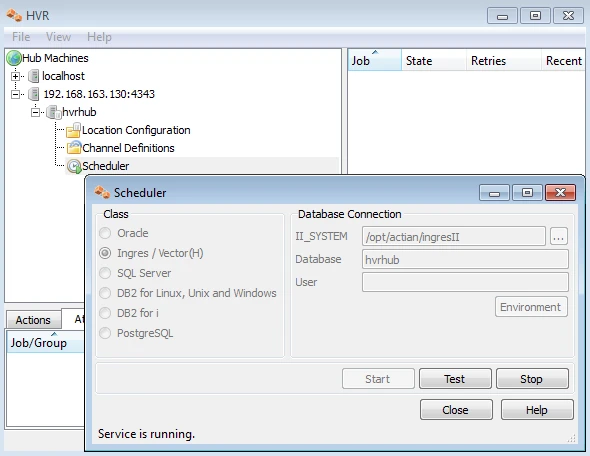
Next, instruct the HVR Scheduler to trigger the replication jobs.
The replication jobs inside the Scheduler each execute a script under $HVR_CONFIG/job/hvrhub/hvr_demo01 that has the same name as the job. So job hvr_demo01–cap–db1 detects changes on database testdb1 and stores these as transactions files on the hub machine.
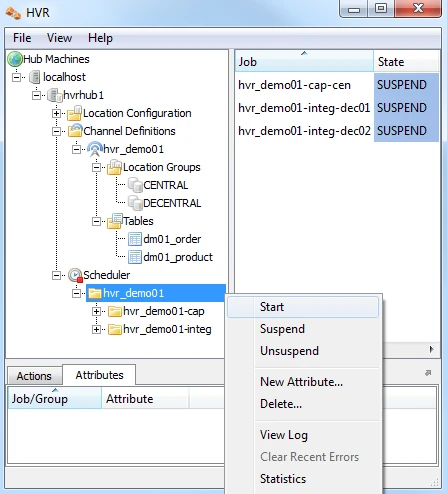
The other two jobs (hvr_demo01–integ–db2 and hvr_demo01–integ–db3) pick up these transaction files and perform inserts, updates and deletes on the two target database.
Test Replication
To test replication, make a change in testdb1:
testdb1/hvr SQL> insert into dm01_product values (1, 19.99, 'DVD'); SQL> commit;
In the HVR log file you can see the output of the jobs by clicking on View Log. This log file can be found in $HVR_CONFIG/log/hubdb/hvr_demo01–cap–db1.
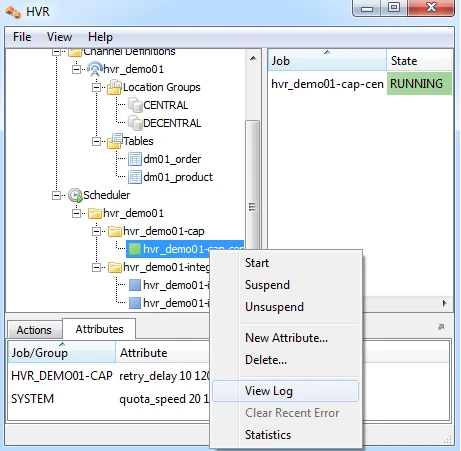
The job output looks like this:
hvr_demo01-cap-db1: Scanned 1 transaction containing 1 row (1 ins) for 1 table. hvr_demo01-cap-db1: Routed 215 bytes (compression=40.6%) from 'db1' into 2 locations. hvr_demo01-cap-db1: Capture cycle 3. hvr_demo01-integ-db2: Integrate cycle 2 for 1 transaction file (215 bytes). hvr_demo01-integ-db2: Integrated 1 change from 'dm01_product' (1 ins). hvr_demo01-integ-db2: Integrate used 1 transaction and took 0.004 seconds. hvr_demo01-integ-db3: Integrate cycle 2 for 1 transaction file (215 bytes). hvr_demo01-integ-db3: Integrated 1 change from 'dm01_product' (1 ins). hvr_demo01-integ-db3: Integrate used 1 transaction and took 0.013 seconds. hvr_demo01-integ-db3: Waiting...
This indicates that the jobs replicated the original change to testdb2 and testdb3. A query on testdb2 confirms this:
testdb2/hvr SQL> select * from dm01_product;
| prod_id | prod_price | prod_descrip |
| 1 | 19.99 | DVD |
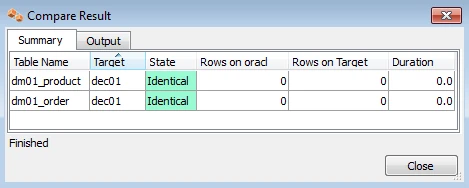
HVR Compare and Refresh
HVR Compare checks whether two locations have identical rows, and HVR Refresh copies the content of one location to the second location. In the HVR GUI, right-click on a channel and select HVR Compare (or HVR Refresh). Choose source and target locations.
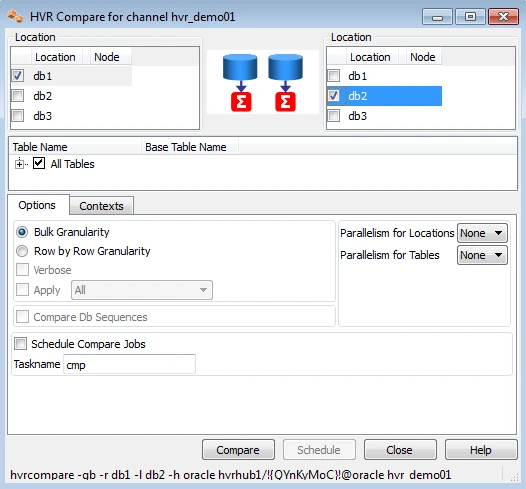
The outcome of the comparison is displayed below;