Activating Replication
Option Activate Replication allows you to create objects needed for replication runtime, and start data replication between source and target locations within a channel. The objects include replication jobs that are managed by the Scheduler, scripts, state tables, subdirectories, files, etc.
Option Activate Replication corresponds to the hvractivate CLI command.
The option to activate replication is available on the following pages:
- Channel Details: the Activate Replication button at the top right of the page.
- Locations: the Activate Replication option under the More Options menu
 at the top right of a page.
at the top right of a page. - Location Details: the Activate Replication option under the More Options menu
 related to each channel in the Channel Membership pane.
related to each channel in the Channel Membership pane. - Create New Channel: option Activate Replication on step 5 of channel creation workflow.
- Tables: the Activate Replication option under the More Options menu
 at the top right of a page.
at the top right of a page. - Table Details: the Activate Replication option under the More Options menu
 at the top right of a page.
at the top right of a page. - Event Details: (related to the activate event): the Repeat Activate Replication button at the top right of the page.
The Activate Replication option may appear disabled in certain cases, for example, on the Channel Details page, if no locations are added to a channel. On the Tables page, you need to select a channel in the Channels selector and one or more tables to enable the option, etc. When you hover over the disabled option, a tooltip will appear with an appropriate explanation.
Clicking the Activate Replication option opens the Activate Replication dialog, where you can customize replication components, or change the replication settings if the replication was already activated. For detailed information about each of the options available in the dialog, see section Activate Replication Options below.
Clicking the Activate Replication button in the Activate Replication dialog will start the activation job. You will see the following notification.
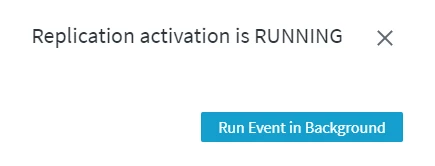
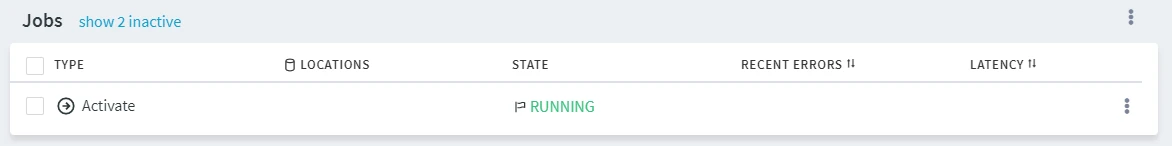
On the Channel Details page, the state of the Activate job is displayed on the Jobs pane. To see the details of this Activate event, click the More Options icon ![]() related to the job and select Go To Event.
related to the job and select Go To Event.
Activate Replication Options
The following options for configuring activation of replication are available in the Activate Replication dialog.
Locations
The Activate Replication dialog, by default, activates replication for all locations in a channel. These defaults are perfect for the first-time activation of the channel, but are rarely the correct defaults to use when the channel was activated before. Replication activation completes faster if it only runs for a limited set of locations. You can select specific locations for which replication will be activated. It is recommended to select only those locations that are affected by a change to the channel. For example, if a change has been made to a capture location group, you only need to select the source location(s).
In the Command Line Interface, this option corresponds to hvractivate -l.
Tables
The Activate Replication dialog, by default, activates replication for all tables in a channel. You can select specific tables for which the replication will be activated. It is recommended to select only those tables that are affected by a change to the channel. For example, if a new table has been added to the channel, activate replication (with Table Enrollment and Supplemental Logging (if applicable) components) for the new table only.
In the Command Line Interface, this option corresponds to hvractivate -t.
Replication Components
Specific replication components only affect certain types of objects required for capture and integration. HVR analyzes the channel definition, source and target locations, actions defined in the channel or changes made to channel definition, and automatically displays and selects the components that are relevant to the channel. For example, the File Location State component is displayed in the Activate Replication dialog only for the channels with file systems locations. Below are the individual replication components, their meaning, and whether or not they should be selected when activating replication.
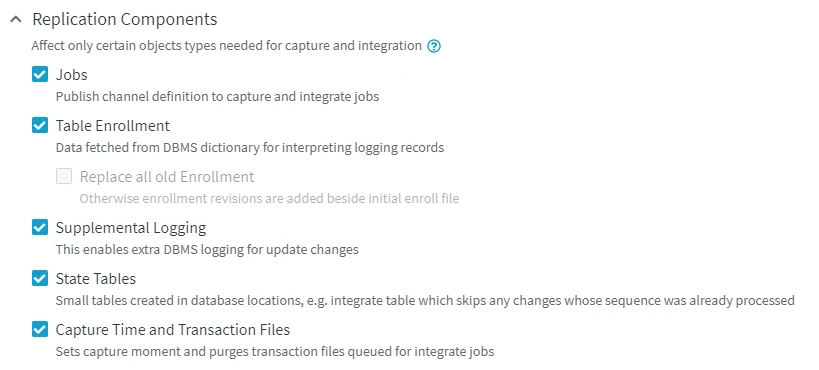
Jobs
The Jobs component registers replication jobs under the Scheduler (and in the respective repository tables). After changing a channel definition, jobs must always be recreated. We recommend you always do this when there has been any change to the channel.
In the Command Line Interface, this option corresponds to hvractivate -oj.
Database Triggers
The Database Triggers component is available if trigger-based capture method (Capture_Method=DB_TRIGGER) is defined on a source location.
The trigger-based capture method has been deprecated since 6.2.0/0.
The Database Triggers component is relevant only for trigger-based capture scenarios. Triggers call database stored procedures created by HVR. Database triggers must be recreated each time the table definition changes. Re-creating triggers is never a problem but may take time if otherwise unnecessary. Select only tables that require an updated trigger definition when (re)creating triggers for trigger-based capture.
If the Database Triggers component is enabled, but the goal is to perform log-based capture, then check the channel definition because there may be an error in the capture action.
For the list of locations that support the trigger-based capture, see section Capture in Capabilities.
In the Command Line Interface, this option corresponds to hvractivate -ot.
Database Procedures
The Database Procedures component is available if:
Trigger-based capture method (Capture_Method=DB_TRIGGER) is defined on a source location.
The trigger-based capture method (Capture_Method=DB_TRIGGER) has been deprecated since 6.2.0/0.
Action Integrate with parameter DbProc is defined on a target location.
The Database Procedures component is relevant for a source location with trigger-based capture defined, and for a target location if parameter DbProc of action Integrate is defined. HVR (re)generates the programming code for stored procedures that are invoked by the triggers, and by the integrate job for scenarios using parameter DbProc of action Integrate. Database procedures must be (re)created each time the table definition changes. Select only the modified tables to speed up the creation/compilation of the stored procedures. Note that for trigger-based capture, database procedures require state tables in the source database. If the database is Oracle, then the user of that location must have the execute privileges on DBMS_ALERT. Without these related objects and privileges, the generated programming code will fail to compile resulting in error messages.
For the list of locations that support parameter DbProc of action Integrate, see section Integrate in Capabilities.
The procedures rely on the existence of a table (and the correct definition in sync with the table definition in the channel) in order to compile successfully. For every table, three database procedures are created for insert, update, and delete, unless the table has no primary key, in which case only the delete and insert procedures are created (and the updates are executed as a delete of the old row followed by an insert of the new row).
In the Command Line Interface, this option corresponds to hvractivate -op.
Change Tables
The Change Tables component is available if:
Trigger-based capture method (Capture_Method=DB_TRIGGER) is defined on a source location.
The trigger-based capture method (Capture_Method=DB_TRIGGER) has been deprecated since 6.2.0/0.
Action Integrate with parameters OnErrorSaveFailed or Method=Burst is defined on a target location.
Action CollisionDetect is enabled.
Depending on the use case, the Change Tables component can only affect the source database or target database locations.
In the source database location(s), the Change Tables component creates two tables for each replicated table in a channel. The log-based change data capture does not use change tables on the source.
In the target database location(s), if error tables exist (as a result of defining parameter OnErrorSaveFailed of action Integrate), then the error tables will be dropped during replication activation (filtered based on the tables selected in the list). Error tables are only created when the first error occurs, and not during replication activation. If the CollisionDetect action is defined, history tables will be created or recreated if they already exist. If it is important to keep old error rows or the history of changes for active/active environments, ensure to unselect the Change Tables component when activating replication.
This component will also drop burst tables (tables that end with __b) in a target database that were created as a result of defining parameter Method=Burst of action Integrate. If the integration is in the middle of a burst cycle, i.e. changes were moved into the burst tables but not yet applied to the target tables, then the Change Tables component will drop data that impacts the ability to recover.
In the Command Line Interface, this option corresponds to hvractivate -oc.
Table Enrollment
The Table Enrollment component is only relevant to source database locations that use log-based capture. HVR generates an enroll file listing all tables in the channel, their database object identifiers and column information in order to perform log-based change data capture. The information to generate this file is queried out of the database dictionary.
To ensure the enrollment information is up-to-date, the component Table Enrollment must be selected every time when either of the following have changed:
- Table definitions in the channel definition
- Settings related to the database transaction log reading or location (in the channel definition or through database settings).
Regenerating table enrollment is always done for the entire channel and not just for one table, so if the channel includes many tables, obtaining the enrollment information may take some time (this also depends upon on the database speed).
Replace all old Enrollment
The Replace all old Enrollment component recreates (replaces) the enroll file for all tables present in the channel.
In the Command Line Interface, this option corresponds to hvractivate -oe.
File Location State
The File Location State component is only relevant for file locations. This option resets the directory _hvr_state in a file location.
In the Command Line Interface, this option corresponds to hvractivate -of.
Publication
Since v6.2.5/0
Publication is required for capturing from PostgreSQL using Logical Replication since 6.2.5/0. HVR will run CREATE PUBLICATION to add a new publication into the source PostgreSQL database. For more information, see Generic PostgreSQL Configuration section in PostgreSQL Requirements.
In the Command Line Interface, this option corresponds to hvractivate -ou.
Supplemental Logging
Supplemental logging is required to ensure the accurate replication of table updates using SQL statements in the target database. Supplemental logging ensures that for every update to a row, the database includes (at least) the primary key column data in the log. Different databases use different mechanisms and terms to enable supplemental logging.
The Supplemental Logging component is only relevant for source database locations when log-based capture is defined. This component will enable supplemental logging on source tables as needed depending on the channel definition. HVR will implement as granular supplemental logging as possible, but many options in the channel, as well as the features of the database, determine whether full supplemental logging on all columns or only for a subset of columns is required, e.g. the primary/unique key.
For Oracle location, the Supplemental Logging component will not drop the supplemental logging during replication deactivation, since HVR does not know if other software relies on the supplemental logging that HVR may or may not have created.
Validating whether the correct supplemental logging is in place can take a significant amount of time – proportional to the number of tables in the channel. So, if no tables have been added to the channel and no tables were dropped and recreated in the source database, then unselect this component when activating replication. If only a few tables were added and others already had supplemental logging added, then consider selecting only the tables that still need supplemental logging to speed up replication activation.
In the Command Line Interface, this option corresponds to hvractivate -ol.
State Tables
State tables are tables that HVR uses for processing purposes and are only relevant for database locations. The State Tables component creates state tables in the target databases. They are used to track replication so that in the event of a loss of network connectivity to the target or some crash, we can accurately resume replication from where it left off. By default, state tables are also used to prevent transaction loopback in an active/active setup. State tables also contain recovery information that enables loss-less recovery in case of a failover, even if the entire hub was lost.
In a source database location, state tables are only created for trigger-based capture scenarios: one toggle table called hvr_togchn, and one sequence table called hvr_seqchn. Log-based change data capture does not use state tables on the source database.
The trigger-based capture method (Capture_Method=DB_TRIGGER) has been deprecated since 6.2.0/0.
In the target database location, the tables are hvr_ibchn[_]loc, hvr_ischn[_]loc, and hvr_icchn[_]loc (with the channel name substituted for chn and the location name for loc). The state tables contain the commit time and transaction information and get updated every time HVR applies transactions to that location to ensure that no transactions are lost, but none are applied more than once. Generally, after creating state tables, they do not need to be re-created. But if this option is selected, they will be re-created, and the state data stored in the tables will be lost. Do not recreate the state tables if an error occurred such as the network connection between the hub and the destination was temporarily lost, or if a capture rewind was performed yet transactions should not be applied again to the target.
In the Command Line Interface, this option corresponds to hvractivate -os.
Capture Time and Transaction Files
The Capture Time and Transaction Files component creates a capture state file that maintains the position in the log and where to read from. By default, when selecting this component, the capture time will be Now, but capture rewind is available if during testing you want to go back or forward through the transaction stream (as long as the backups of the transaction log exist).
For a source database location, the Capture Time and Transaction Files component (re)creates a capture state file. HVR will start capturing transactions that modify tables in the channel after the initial capture time. By default, the capture time is current.
Resetting the capture time is often not desirable because any open transactions that HVR may have been tracking will be lost. If the capture is reset, then typically a database has to be run in order to re-synchronize tables if the capture time was reset. We will give a warning if the capture time is reset. Unselect the Capture Time and Transaction Files component to prevent the capture time from being reset.
The Capture Time and Transaction Files component does not affect a database target location.
In the Command Line Interface, this option corresponds to hvractivate -or.
Capture Start Moment
Capture start moment (rewind time). Activate the channel to start capturing changes from a specific time in the past, rather than only changes made from the moment the replication is activated. Capture rewind time is only supported for database log-based capture (not for trigger-based capture) and for capture from file locations when parameter DeleteAfterCapture is not defined.
The Capture Start Moment option is enabled only when the Capture Time and Transaction Files option is selected.
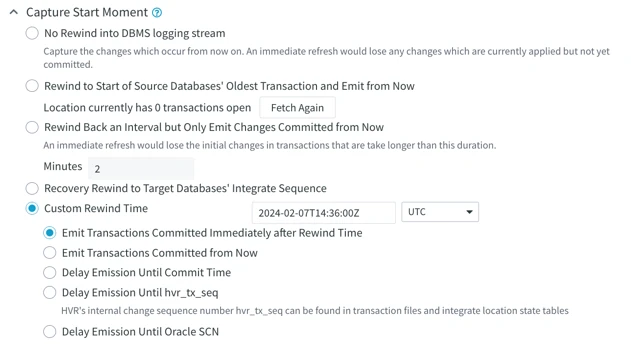
In the Command Line Interface, this option corresponds to hvractivate -i.
No Rewind into DBMS logging stream
Capture the changes which occur from now on. An immediate Refresh would lose any changes which are currently applied but not yet committed.
Rewind to Start of Source Databases' Oldest Transaction and Emit from Now
Capture changes from the beginning of the oldest current (not closed) transaction and emit from now. Transactions that do not affect the table of the channel will not be considered.
Rewind Back an Interval but Only Emit Changes Committed from Now
Rewind Back an Interval means capture rewinds back an interval of minutes. For example, if the interval is 1 minute, the capture will rewind back 1 minute and capture changes that happened up to 1 minute ago, but Only Emit Changes Committed from Now means that although capture rewinds back 1 minute, it will only emit (send to a target location) changes that were committed after now (current date and time). For example, a change that happened 55 seconds ago and was committed 50 seconds ago will not be emitted, therefore not replicated.
Recovery Rewind to Target Databases' Integrate Sequence
This option is meant to be used in a hub failover scenario. The channel definition before and after the failure should be identical (action definition and tables) for this option to work successfully. This option uses data from the integrate state table filled by the last Integrate job.
Note that activating target location(s) with option state tables will destroy the state in the state tables. For this reason you must initialize the capture time separately without the state tables. Upon such failover it is recommended to not re-initialize with option state tables.
Clicking the Fetch Sequence button opens a dialog with a few options available:
Previous channel used different names: for when the channel name has been changed. The previous channel or location names can be entered.
Select integrate locations: for when the source or target locations have been changed in the new setup. Select the required integrate locations. For multiple selected targets, rewind will be done to the oldest integrate sequence.

Custom Rewind Time
Define the time for emitting transactions. The emit time refers to the point at which changes will be sent from the capture location to the integrate location. The emit time may differ from the Capture Start Moment for a system with long-running transactions. HVR will start capturing changes to the tables in the channel only from the capture time forward. However, in order to fully capture long-running transactions in the system, you may want to start capture earlier and emit only from some point forward. ERP systems in an Oracle database often have long-running transactions, but long-running transactions are not common in many other databases.
There are several scenarios when the Capture Start Moment option is selected as part of replication activation, but a “reset” (i.e. Refresh) is not required. For example, if a source database is upgraded from one version to another while the application is not running. Upgrading a database often results in a lot of transaction log changes, and regardless of whether HVR can read those changes without any issues, it may just be cleaner to suspend the capture during the upgrade. It is also possible that the database will be restarted as part of the upgrade, probably more than once. Then, after the upgrade, you will perform a capture rewind to a current point (or to the point in time after the upgrade but, before starting the application) to skip over the transaction log changes during the upgrade. In such a scenario, you would know that you have not missed any changes to the application.
Another example would be an application upgrade with downtime, during which, depending on the upgrade, there will be also no changes to the tables you want to replicate. Of course, in some cases, there are table changes (DML and/or DDL) made during an application upgrade that may or may not need to be reflected as part of the replication.
If old transaction logs are still accessible on the server after a restart, then HVR can continue to run through the old sequence of transaction logs until it needs to resume back at the reset point. Replication needs to be re-activated when getting to the point when the reset happens to be able to continue. If the transaction logs are no longer available from before the server restarts, then Refresh is required to get the data back in sync. Always use Compare to identify the damage which, depending on the change rate on the application, may be more or less difficult to achieve.
Available options are:
- Emit Transactions Committed after Rewind Time: Emit changes from the specified Custom Rewind Time.
- Emit Transactions Committed from Now: Emit changes from now.
- Delay Emission Until Commit Time: Emit changes from a specified moment of time.
- Delay Emission Until hvr_tx_seq: Emit changes from a specified transaction sequence number. The number can be given in a decimal or a hexadecimal format. If the number contains decimal digits, only then it is decimal. Otherwise, if it starts with prefix 0x or contains hexadecimal digits A, B, C, D, E, or F, then it is treated as hexadecimal.
Since 6.1.5/5, this option is not supported for Db2 for Linux, Unix, and Windows configured with Database Partitioning Feature (DPF).
- Delay Emission Until Oracle SCN: Emit changes from a specified system change number (SCN). For Oracle, this is equivalent to Emit from the transaction sequence number where hvr_tx_seq=scn*65536. The number can be in a decimal or a hexadecimal format.
Advanced Activation Options
Location Parallelism
During replication activation, we can manage multiple locations in a channel. The Location Parallelism option controls if per-location processes (creating integrate state tables on a Snowflake target location, checking table IDs from capture location, enabling supplemental logging on an Oracle source location) will be done in parallel or not. Especially for capture locations, enabling supplemental logging takes a significant amount of time. The Location Parallelism option reduces the time it takes to deal with the processes.
Show Equivalent HVR Command Line
Show the CLI command equivalent to the UI options selected in the dialog. You can use (copy and paste) the equivalent line to manually repeat or perform this operation later on.
In cases when the command line equivalents are different for Linux/Unix and Windows, both options are shown. Select option Include -R (Remote hub server) argument to include the parameters for accessing a hub server that runs on a remote machine. For more information about this CLI option, see hvractivate -R.
Refresh Data into Target After Activation
Load data selected from a source location to a target location.
Force Start Replication Jobs
Start the Capture job after the replication is activated. After the first capture cycle, the Refresh is started. When the refresh is complete, the Integrate job is started. If this option is not selected, the capture and integrate jobs will have the SUSPEND state after the replication activation.
In the Command Line Interface, this option corresponds to hvractivate -J.