Replication with File Locations
This section describes how to set up and use files as a source or target in Fivetran HVR replication.
File Replication Scenarios
HVR supports three types of managed file transfers:
Database-to-File Replication
In a database-to-file transfer, data is read from a source database and copied into one or more files on the target file location. By default, the resulting files are in the HVR XML format preserving the table information. However, other formats are supported through the FileFormat action, which you define when creating a channel.
File-to-File Replication
A file-to-file transfer involves copying files from one source file location to one or more target file locations. A file location can be a directory or a tree of directories, which can either be accessed through the local file system (Unix, Linux or Windows) or a network file protocol (FTP, FTPS, SFTP, or WebDAV). Files can be copied or moved. In the latter case, the files are deleted from the source after they have been copied to the target location.
To distribute sets of files, HVR provides the possibility to copy files selectively from the source location by matching their names to a predefined pattern. This feature also enables the routing of files within the same source location to different target locations based on their file names to enable selective file distribution scenarios.
In the file-to-file replication scenario, HVR treats each file as a sequence of bytes without making an assumption of their file format.
File-to-Database Replication
In a file-to-database transfer, data is read from files in a source file location and replicated into one or more target databases. Typically, source files are expected to be in a specific HVR XML format containing table information required to determine to which tables and rows the changes should be written in the target database. It is also possible to use other input file formats by including an additional transformation step in the file capture.
The create channel flow does not support a file-to-database scenario. A file-to-database scenario requires manual configuration with the correct actions. Select the Basic channel without locations option when you select channel type in step 1.
Supported File Locations
HVR supports the following file storage locations:
- Azure BlobFS
- Azure Data Lake Store
- FTP
- SFTP
- Google Cloud Storage
- HDFS
- S3
For the requirements, access privileges, and other features of HVR when using one of the listed locations, see the corresponding requirements pages:
- Amazon S3 Requirements
- Apache HDFS Requirements
- Azure Blob Storage Requirements
- Azure Data Lake Storage Requirements
- Google Cloud Storage Requirements
- File, FTP, SFTP Requirements
Location Connection
The locations can be local or remote. A local location is just a directory or a tree of directories on your file system.
There are two ways to connect to a remote location that can be used simultaneously:
- Connect to a remote HVR Agent through HVR's built-in protocol.
- Connect through an external protocol (e.g. FTP, SFTP, WebDAV, HDFS or S3). For more information, see sections Amazon S3 Requirements, and File, FTP, SFTP Requirements. The advantage of using these protocols is the monitoring and managing capabilities HVR provides.
Channel Configuration
There are two types of channels that can be configured for file replication scenarios:
- A channel containing only file locations (with no table information). In this case, HVR handles captured files as 'blobs' (a stream of bytes). Blobs can be of any format and can be integrated into any file locations. If only actions Capture and Integrate (no parameters) are defined for a file-to-file channel, then all files in the source directory (including files in sub-directories) are replicated to the target directory. The original files are not deleted from the source directory and the original file names and sub-directories are preserved in the target directory. New and changed files are replicated, but empty sub-directories and file deletions are not replicated.
- A channel containing a file location as a source and a database table as a target or vice versa. HVR interprets each file as containing database changes in XML, CSV, Avro, JSON or Parquet formats. The default format for file locations is HVR's own XML format. In this case, HVR can manage data in the files.
Replication Options
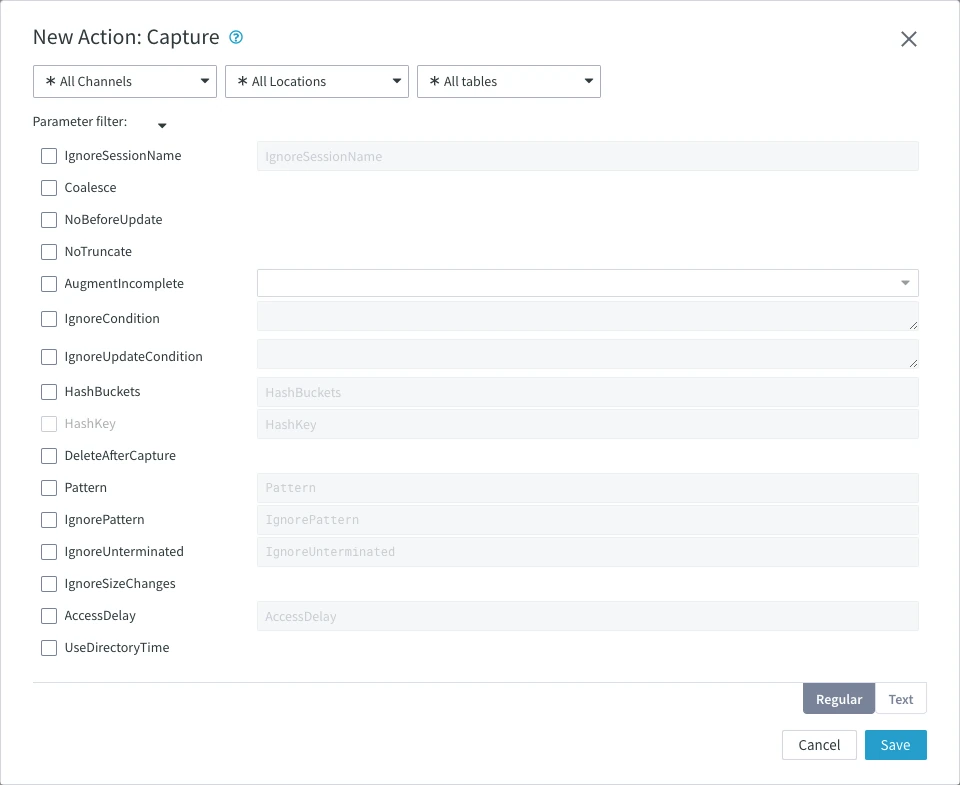
Action Capture is sufficient to start replication, it instructs HVR to capture files from the source location. However, you can configure the capture behavior according to your needs by setting certain Capture parameters. For example, use parameter DeleteAfterCapture to move files instead of copying them. The parameters Pattern and IgnorePattern allows you to control which files are captured and/or ignored during replication: you can specify to capture all files with the *.xml extension and ignore all files with *tmp* in their name. More powerful expressions are supported by HVR. For more options, see section Capture.
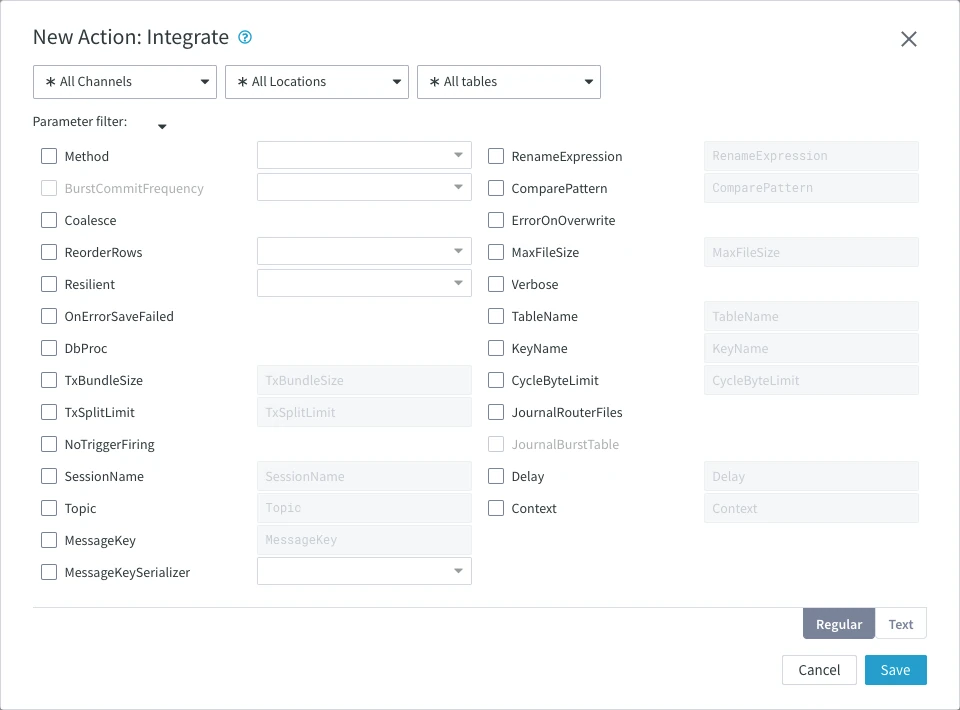
Action Integrate should be defined for the target location and it is sufficient to commence file transfer. However, as with action Capture, you can configure several parameter to impart specific behavior during integration. For example, the parameter ErrorOnOverwrite controls whether overwrites are allowed or not. Overwrites usually happen when a source file is being altered and HVR has to transfer it. The parameter RenameExpression allows you to rename files using regular expressions (e.g. {hvr_op}). The {hvr_op} expression adds an operation field enabling deletes to be written as well, which is useful in database/file transactions. The parameter MaxFileSize can be used on structured files to bundling rows in a file (split files). For more options, see section Integrate.
File Transformation
HVR supports a number of different built-in transformation mechanisms that are applied when data is captured from a source and before it is integrated into a target:
- Soft deletes (introduction of a logical delete column, which indicates whether a row was deleted on a source database)
- Transforming XML from/into CSV
- Tokenize (calling an external token service to encrypt values)
- File2Column (loading a file into a database column)
For more information, see section Transform.
Integrate Limitations
By default, for file-based target locations, HVR does not replicate the delete operation performed at the source location. Use replication style TimeKey to reflect the delete operation in target files.