Amazon RDS PostgreSQL Setup Guide
Follow these instructions to replicate your Amazon RDS PostgreSQL database to your destination using Fivetran.
Prerequisites
To connect your Amazon RDS PostgreSQL database to Fivetran, you need:
- PostgreSQL version 9.6 - 17
- An RDS account with an account administrator role
- Access to your database server
- Access to your database host's machine
- Your database host's IP (for example,
1.2.3.4) or domain (your.server.com) - Your database's port (usually
5432) - TLS enabled on your database. Follow the Amazon TLS setup instructions to enable TLS on your database.
- (If you want to connect using SSH) An SSH server
Setup instructions
Choose connection method (TLS required)
You must have TLS enabled on your database to connect to Fivetran.
Decide whether to connect your database to Fivetran directly, using an SSH tunnel, using AWS PrivateLink, or using Proxy Agent. How you configure your security groups in later steps will differ depending on this decision. For AWS PrivateLink and Proxy Agent you must follow their dedicated setup guides.
Connect directly
Connect directly
Fivetran connects directly to your database instance. This is the simplest method.
If you connect directly, you will create a rule in a security group that allows Fivetran access to your database instance.
Connect using SSH
Fivetran connects to a separate server in your network that provides an SSH tunnel to your database. You must connect through SSH if your database is in an inaccessible subnet.
If you connect using SSH, you will configure your SSH tunnel server's security group to allow Fivetran access and configure your database's security to allow access from the tunnel.
Before you proceed to the next step, you must follow our SSH connection instructions.
Connect using AWS PrivateLink
Connect using AWS PrivateLink
You must have a Business Critical plan to use AWS PrivateLink.
AWS PrivateLink allows VPCs and AWS-hosted or on-premises services to communicate with one another without exposing traffic to the public internet. PrivateLink is the most secure connection method. Learn more in AWS’ PrivateLink documentation.
Follow our AWS PrivateLink setup guide to configure PrivateLink for your database.
Connect using Proxy Agent
Fivetran connects to your database through the Proxy Agent, providing secure communication between Fivetran processes and your database host. The Proxy Agent is installed in your network and creates an outbound network connection to the Fivetran-managed SaaS.
To learn more about the Proxy Agent, how to install it, and how to configure it, see our Proxy Agent documentation.
Create read replica (optional)
Connect Fivetran to a read replica to avoid putting load on your primary database. A replica helps Fivetran sync your data without affecting the queries running on your primary database. We recommend using a read replica, but it is not required.
If you prefer to connect Fivetran to your primary database, or if you already have a read replica configured, proceed to the next step.
To use a read replica, your database must run PostgreSQL 16 or later, or you must use Query-Based as your incremental sync method.
Expand for instructions
For more instructions, see the AWS creating a read replica documentation.
In your Amazon RDS Dashboard, select the PostgreSQL instance you want to replicate.
In the instance details page, click Actions > Create read replica.
In DB instance identifier, enter a unique name for the replica (for example,
pg-read-fivetran).In DB instance class, choose a size appropriate for expected read load (it can be smaller than the primary).
In Connectivity > Public access:
- Select Publicly accessible only if you chose to connect directly.
- Select Not publicly accessible if you chose to connect using SSH, AWS PrivateLink, or Proxy Agent.
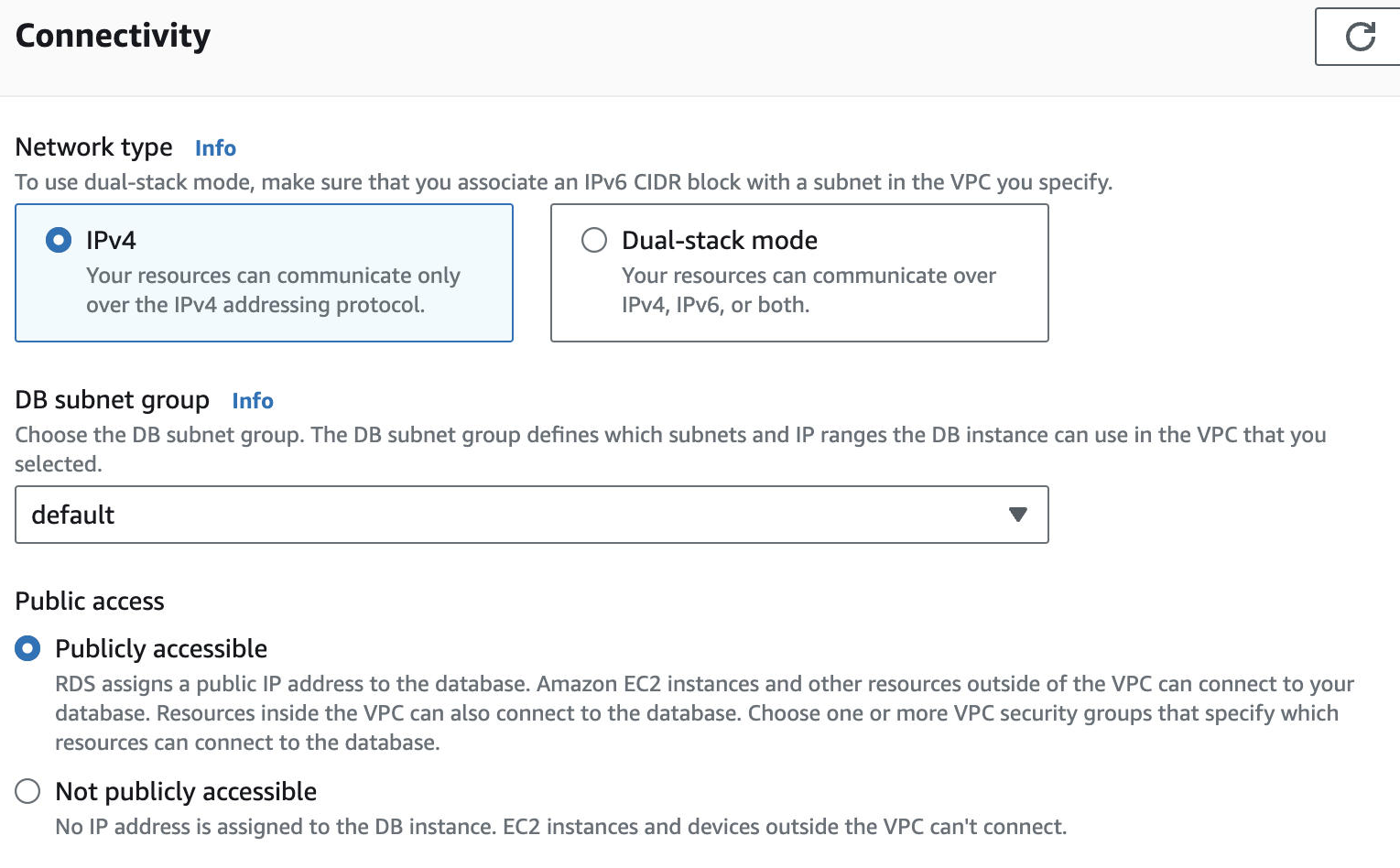
In Additional configuration > DB parameter group, attach (or create and attach) a parameter group that sets
max_standby_streaming_delayto 15–30 minutes (900000–1800000 ms). This ensures that import/incremental queries complete before the replica server cancels them.At the bottom of the page, click Create read replica and wait for the status to change from
creatingtoavailable.
Enable database access
Complete the access configuration steps on the database instance that Fivetran will connect to, either the read replica or the primary.
Grant the Fivetran data processing servers access to your database instance. How you configure access depends on whether your instance is in a VPC:
If your instance is in a VPC, configure the instance's VPC security group to allow Fivetran to connect. If your organization also uses custom VPC network ACLs, make sure they allow the same traffic that you allowed in the security group. For more information, see the AWS VPC network ACLs documentation.
If your instance is not in a VPC, configure the database security group to allow Fivetran to connect.
AWS has deprecated non-VPC deployments and strongly recommends migrating RDS instances into a VPC. For more information, see the Amazon VPC documentation.
Configure security group
These instructions apply when you connect directly or through an SSH tunnel. If you use the AWS PrivateLink or Proxy Agent connection methods, you already configured their networking settings in the Choose connection method step.
In your Amazon RDS dashboard, click on the database instance you want to connect to Fivetran.
In the Connectivity & security section, find the database's port number and make a note of it. You will need the port number to configure Fivetran.
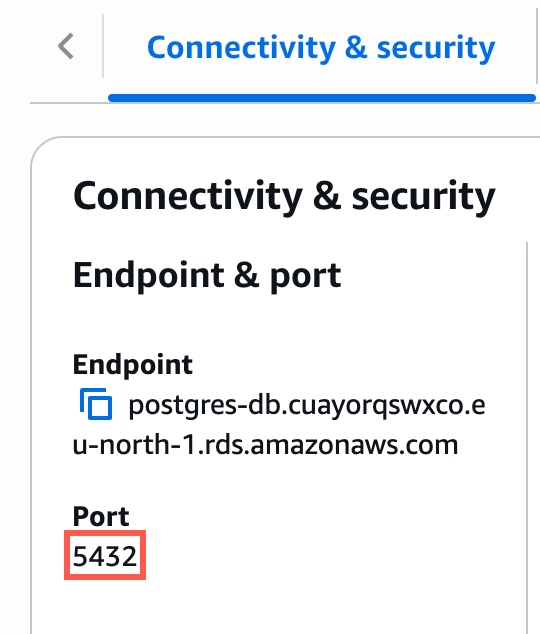
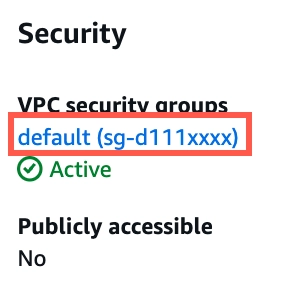
In the Security column, click the link to the database instance's security group.
In the Security Groups panel, select the security group you want to edit, click Actions, and then select Edit inbound rules.
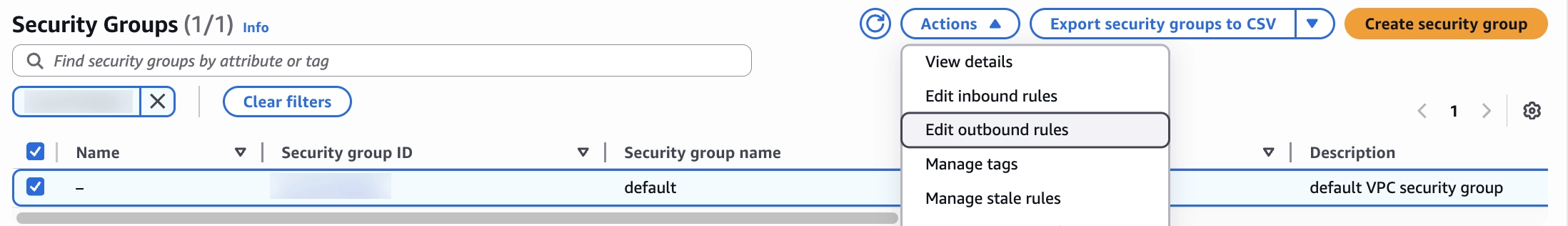
In the Inbound rules section, scroll to the bottom of the list and click Add Rule. A new rule row appears.
In the new rule row, configure the rule:
In the Port Range field, enter your database instance's port number. Use the port you noted in step 2 above. By default, Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL uses port
5432unless you changed it.In the Source field, choose Custom and then enter a value based on your connection method:
- If you're connecting directly, enter the Fivetran IPs for your database's region.
- If you're connecting using an SSH tunnel, enter
{your-ssh-tunnel-server-ip-address}/32.
(Optional) In the Description field, enter a brief note to identify the rule.
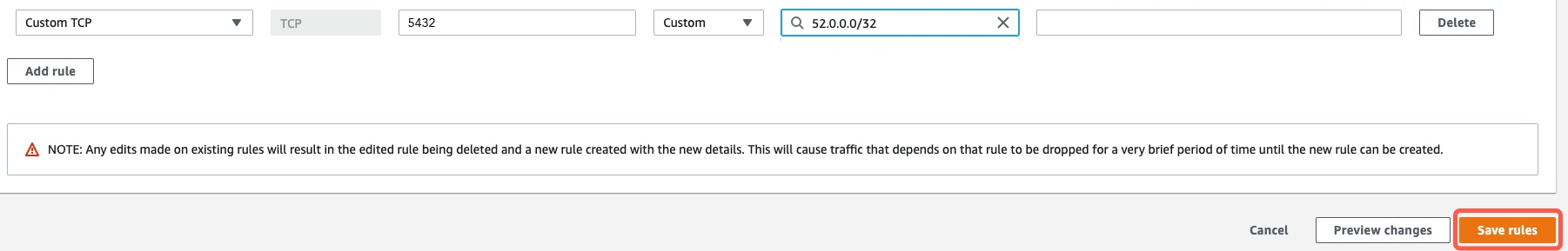
Click Save rules.
Create user
Create a database user for Fivetran's exclusive use.
Connect to your Amazon RDS PostgreSQL database.
Create a dedicated user for Fivetran by running the following SQL command. Replace
<username>and<password>with a username and password of your choice.CREATE USER <username> PASSWORD '<password>';
Grant user read-only access
Grant the Fivetran user read-only access to all tables by running the following commands. To grant access to a schema other than PostgreSQL's default public schema, replace public with the schema name.
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA "public" TO <username>;
GRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA "public" TO <username>;
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES IN SCHEMA "public" GRANT SELECT ON TABLES TO <username>;
The ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES command ensures that future tables created in the schema are also accessible to Fivetran.
If you want to grant access to multiple schemas, run these three commands for each schema.
Restrict access to tables (optional)
If you prefer to limit Fivetran's access to your tables, grant permissions only on the tables that you want to sync. You must grant access table by table; you cannot grant access to a schema and then selectively revoke permissions for a subset of tables.
Ensure that the Fivetran user has access to the schema that contains your table(s).
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA "some_schema" TO <username>;Revoke any previously granted permissions to all tables in that schema.
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES IN SCHEMA "some_schema" REVOKE SELECT ON TABLES FROM <username>; REVOKE SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA "some_schema" FROM <username>;Repeat the following command for each table you want Fivetran to sync.
GRANT SELECT ON "some_schema"."some_table" TO <username>;By default, any tables that you create in the future will be excluded from the Fivetran user's access. To grant access to new tables, run the following command.
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES IN SCHEMA "some_schema" GRANT SELECT ON TABLES TO <username>;
Restrict access to columns (optional)
If you want to limit Fivetran's access to the columns in your tables, grant the Fivetran user access to only certain columns. You must individually grant access for each column that you want to sync.
Ensure that you have revoked any previously granted permission to read all columns in the table.
REVOKE SELECT ON "some_schema"."some_table" FROM fivetran;Grant permission to the specific columns you want to sync (for example,
some_columnandother_column).If you chose Query-Based as your incremental sync method, you must grant us access to the hidden system columns
xminandctid. This speeds up your initial sync and enables capturing deletes.GRANT SELECT (xmin, ctid, some_column, other_column) ON "some_schema"."some_table" TO <username>;
Once you restrict access to columns within a table, the Fivetran user will not have access to any new columns added to that table in the future. To grant access to new columns, you must rerun the command above.
Configure incremental sync method
To keep your data up to date after the initial sync, Fivetran offers multiple incremental sync methods. These methods track recent data changes so Fivetran can sync only what changed since the last sync instead of copying entire tables each time. Learn more in our Updating data documentation.
We recommend using the Logical replication method when possible because it is faster and more efficient than Query-Based. For guidance on choosing the best option for your workload, see Logical replication vs Query-Based documentation.
Configure your chosen incremental sync method:
Logical replication
You can only enable logical replication if your PostgreSQL version is 10 or later. If you want to use logical replication on a read replica, your PostgreSQL version must be 16 or later.
Logical replication is based on logical decoding of the PostgreSQL write-ahead log (WAL). Fivetran reads the WAL using the pgoutput plugin to detect any new or changed data. This plugin replicates from your custom publication without needing additional libraries.
To learn more, see our logical replication documentation.
To enable logical replication, follow these steps:
Go to your Amazon RDS PostgreSQL database.
Ensure that your server has ample free space for the logs. As soon as Fivetran processes a log, we delete it. However, we don't delete logs if the sync is interrupted (for example, if we lose access to your database). In this case, logs may accumulate on your server and consume additional storage. The amount of additional disk space that these logs consume is proportional to the number of changes committed on the server. If we can't resume a lost connection quickly enough and you need more disk space, you can drop the replication slot, which deletes its unconsumed logs.
Set the
rds.logical_replicationparameter to1by following these steps:
i. Create a new parameter group (non-default group).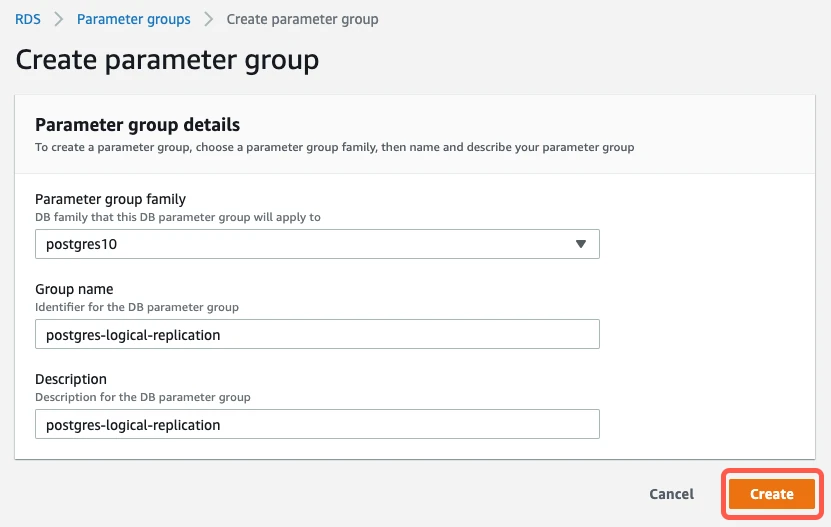 ii. Enable the
ii. Enable the logical_replicationflag in that group by setting the value to1.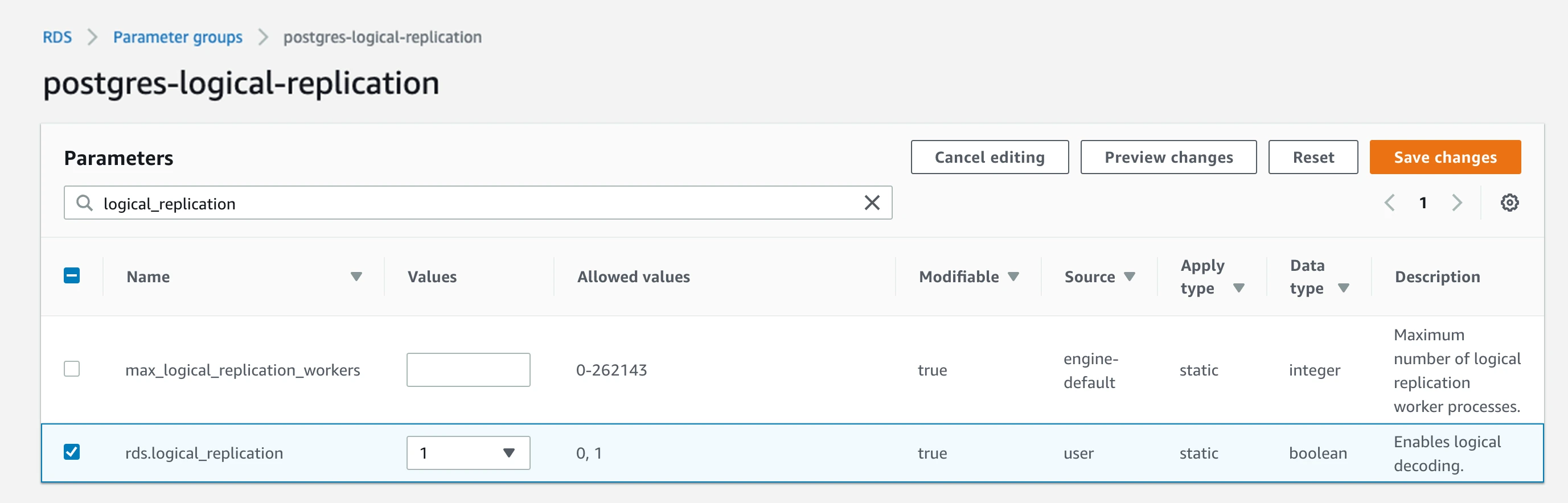 iii. Set
iii. Set wal_sender_timeoutto0.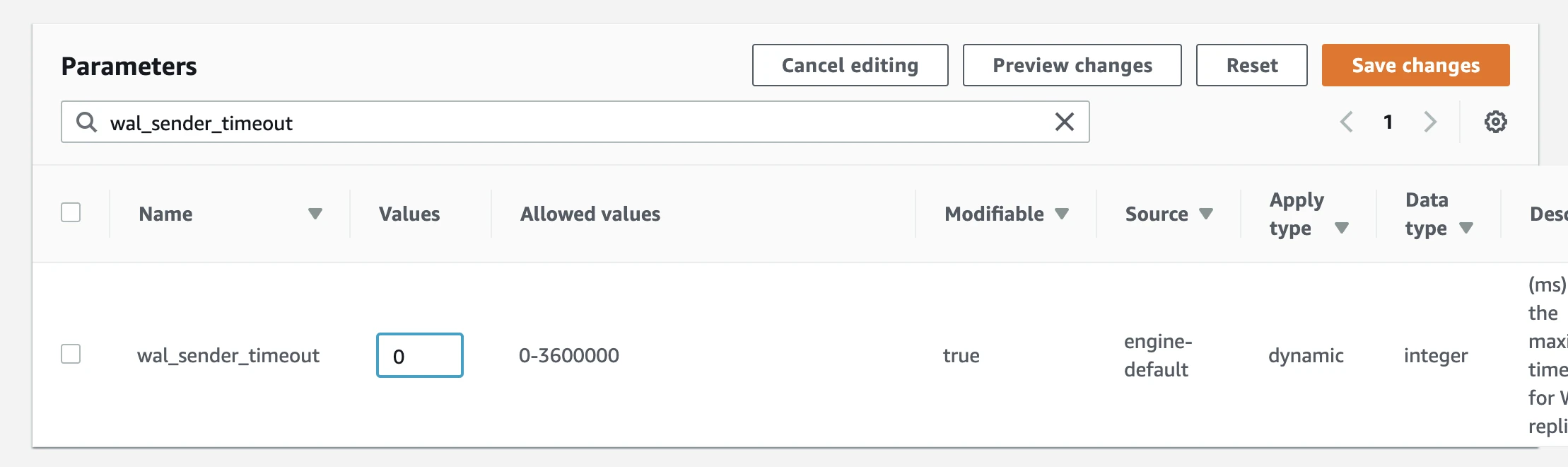 iv. Apply the parameter group to the database.
iv. Apply the parameter group to the database.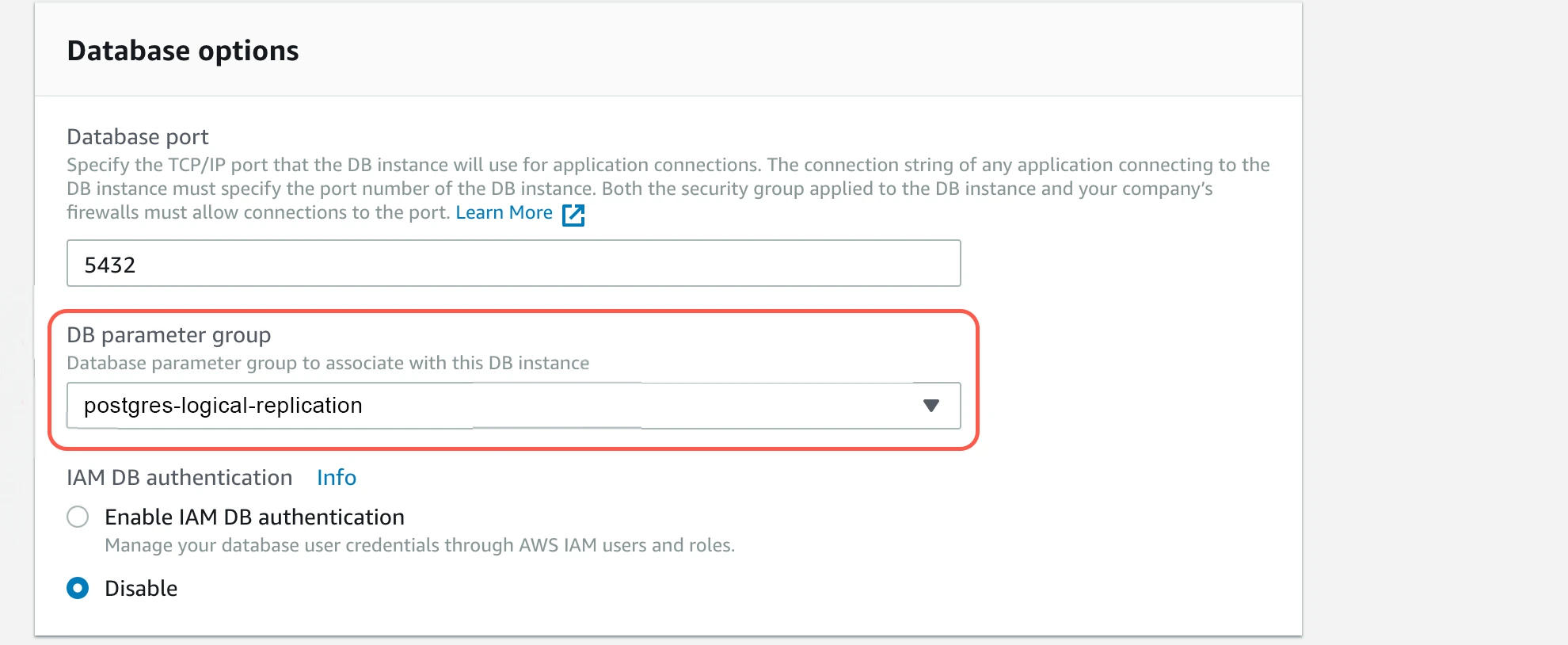
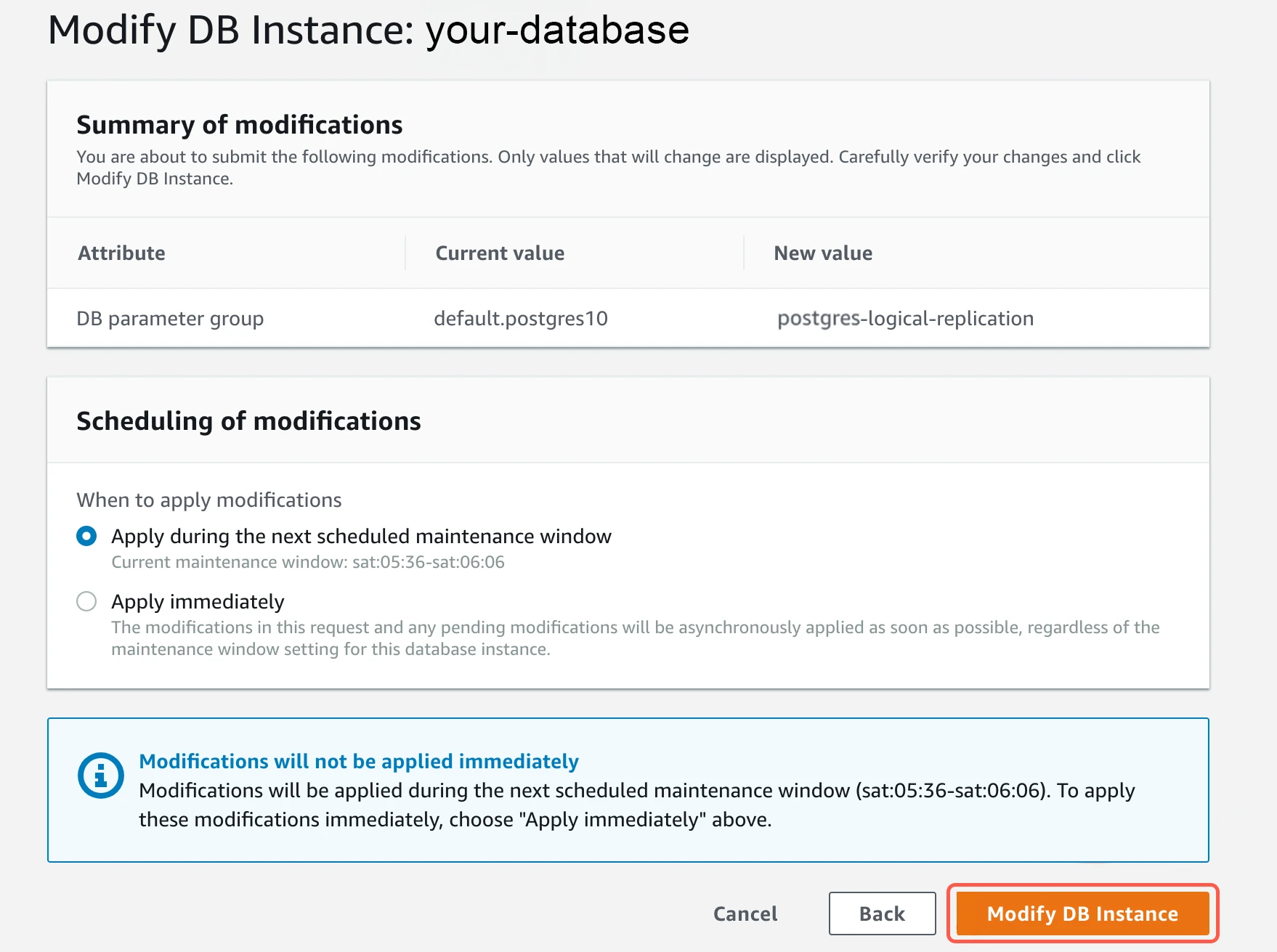 v. Wait until the status changes to
v. Wait until the status changes to pending-reboot, then reboot the database to apply the new parameter group.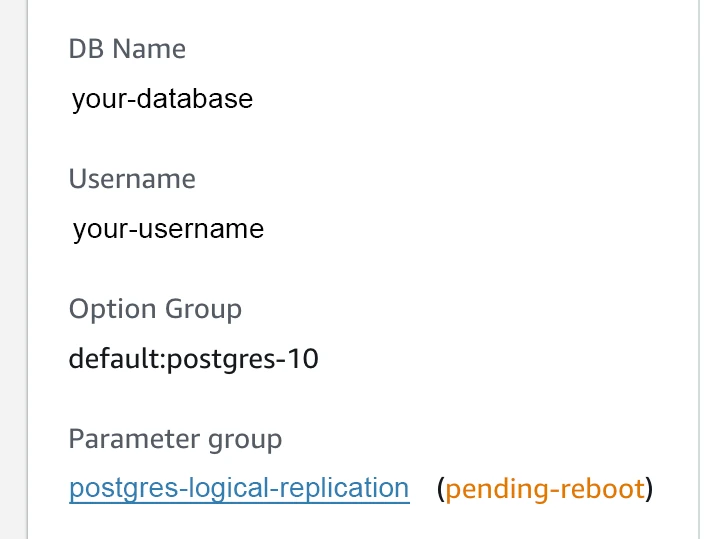
Use a PostgreSQL console (such as a SQL workbench or psql) to log in to your primary database as a superuser. Superusers have the
rds_superuserrole.Create a publication for your tables. If you want, you can create a publication for only certain tables so that you add or remove tables from the publication later on. Only changes from tables in the publication are replicated to Fivetran. Each database can have multiple distinct publications. You must have
CREATEprivileges or above to run this command.The publication name
fivetran_pubquoted throughout this guide is used purely as an example. The actual publication name should be unique for every database and cannot start with a number.CREATE PUBLICATION fivetran_pub FOR TABLE table2, table4, table8;To add or remove a table from a publication, run the following command. You must have ownership rights over the table(s).
ALTER PUBLICATION fivetran_pub ADD/DROP TABLE table_name;Alternatively, you can create a publication for all of your tables. However, you cannot remove any table from this publication later on. You must have superuser privileges to run this command.
CREATE PUBLICATION fivetran_pub FOR ALL TABLES;(Optional) You can choose which operations to include in the publication. For example, the following publication includes only
INSERTandUPDATEoperations.CREATE PUBLICATION insert_only_pub FOR TABLE table1 WITH (publish = 'INSERT, UPDATE');(Optional) To add partitioned tables for PostgreSQL version 13 or later, run the following command to enable
publish_via_partition_root.CREATE PUBLICATION fivetran_pub FOR ALL TABLES WITH (publish_via_partition_root=true);Create a logical replication slot by running the following command. You must use the standard output plugin
pgoutput. Ensure you are connected to the correct database when creating the replication slot; otherwise, your connection will not be able to locate it.You must create a unique replication slot for every connection that uses the same PostgreSQL cluster. Replication slot names cannot start with a number. (The replication slot name
fivetran_pgoutput_slotquoted throughout this guide is used purely as an example.)You need to create the replication slot after you have created the publication.
If your PostgreSQL server version is 16 or later and you want to sync from a standby, create the replication slot based on your deployment type:
- For a cluster deployment, create the replication slot on the primary.
- For a non-cluster deployment, create the replication slot on the standby.
SELECT pg_create_logical_replication_slot('fivetran_pgoutput_slot', 'pgoutput');Verify that your chosen tables are in the publication.
SELECT * FROM pg_publication_tables;Grant the Fivetran user permission to read the replication slot.
GRANT rds_replication TO <username>;Log in as the Fivetran user.
Verify that the Fivetran user can read the replication slot by running the following command. Replace
fivetran_pgoutput_slotwith your replication slot name andfivetran_pubwith the publication name.SELECT count(*) FROM pg_logical_slot_peek_binary_changes('fivetran_pgoutput_slot', null, null, 'proto_version', '1', 'publication_names', 'fivetran_pub');If the query succeeds, then permissions are sufficient.
You must periodically tune the checkpoint_timeout and max_wal_size parameters based on your PostgreSQL database operations. If you do not, you may experience replication failures. To learn how to tune, read this tuning checkpoints documentation.
Query-Based
You can use Query-Based replication for any Amazon RDS PostgreSQL deployment, including a read replica.
Fivetran runs SQL queries that read PostgreSQL system columns (xmin and, when applicable, ctid) to detect new and changed data during each sync.
Capture Deletes (optional)
By default, Query-Based sync detects new and updated rows. If you also want to detect deleted rows, you can turn on Capture Deletes in the connection setup form.
When you enable Capture Deletes:
Fivetran adds an internal helper column
ctid_fivetran_idto each synced table. Fivetran uses this column to track deletes by storing the row'sctidvalue at the end of each sync.- Before the initial sync (new connection): Fivetran creates tables with
ctid_fivetran_idduring the initial sync (no additional re-sync). - After data is already synced (existing connection): Fivetran runs a one-time re-sync of the selected tables to add
ctid_fivetran_id.
- Before the initial sync (new connection): Fivetran creates tables with
This setting is permanent for the connection. After you click Save & Test, it's locked and can’t be disabled later, whether or not the connection has run its first sync.
For details and limitations, see our Capturing deletes documentation.
Query-Based sync requires full table scans to detect updates and may be slower than logical replication, especially for large tables. In high-write databases, PostgreSQL xmin freezing/wraparound can also cause older rows to be re-synced, increasing sync volume and load on your PostgreSQL source database. If possible, use logical replication.
For some accounts, these re-syncs may also increase MAR for that sync. To mitigate this, you can enable pg_visibility and pageinspect and create the required wrapper functions. See our FAQ page for more information.
Fivetran Teleport Sync Sunset
Fivetran Teleport Sync is a proprietary incremental sync method that can add delete capture with no additional setup other than a read-only SQL connection. Updates will be captured using the XMIN system column.
Learn more in our Fivetran Teleport Sync documentation.
If you are trying to connect with a standby or read replica, run the following SQL command on your primary database as the Fivetran user:
CREATE AGGREGATE BIT_XOR(IN v bigint) (SFUNC = int8xor, STYPE = bigint);
If you are not connecting with a read replica, you do not need to do any additional configuration. The aggregate that the Teleport mechanism will later use is automatically created for you.
Finish Fivetran configuration
In your connection setup form, enter a Destination schema prefix of your choice. This name is prefixed to each replicated schema on the destination and cannot be changed once your connection is created.
In the Destination schema names field, choose the naming convention you want Fivetran to use for the schemas, tables, and columns in your destination:
- Source naming: Preserves the original schema, table, and column names from the source system in your destination.
- Fivetran naming: Standardizes the schema, table, and column names in your destination according to the Fivetran naming conventions.
If you want to modify your selection, make sure you do it before you start the initial sync.
Depending on your selection, we will either prefix the connection name to each replicated schema or use the source schema names instead.
Enter your database instance's Port number. The port will be
5432, unless you changed the default.Enter the Fivetran-specific User that you created.
Enter the Password for the Fivetran-specific user.
Enter the name of your Database (for example,
your_database).(Hybrid Deployment only) If your destination is configured for Hybrid Deployment, the Hybrid Deployment Agent associated with your destination is pre-selected for the connection. To assign a different agent, click Replace agent, select the agent you want to use, and click Use Agent.
(Not applicable to Hybrid Deployment) Choose your Connection method.
- If you selected Connect via an SSH tunnel, make a note of the Public Key and add it to the
authorized_keysfile while configuring the SSH tunnel, and provide the following information:- SSH Host: Enter the hostname or IP address of your SSH server. Do not use a load balancer's IP address/hostname.
- SSH Port: Enter the port number of your SSH server. The default port number is
22. - SSH User: Enter the username for SSH access.
- If you selected Connect via proxy agent, choose the necessary proxy agent from the Proxy agents drop-down list (if available) or configure a new proxy agent.
- If you selected Connect via an SSH tunnel, make a note of the Public Key and add it to the
In the Update Method field, select the incremental sync method that you want to use:
- Logical Replication: Enter your Replication Slot name and Publication Name.
- Query-Based: (Optional) Set the Capture Deletes toggle to ON if you want to capture deletes. For more information, see Capture deletes.
In the Destination schema names field, select Fivetran naming or Source naming to determine how the schema names appear in your destination. For more information, see the Schema information section.
(Not applicable to Hybrid Deployment) Copy the Fivetran IP addresses (or CIDR) that you must safelist in your firewall.
Click Save & Test. Fivetran tests and validates our connection to your Amazon RDS PostgreSQL database. Upon successful completion of the setup tests, you can sync your data using Fivetran.
Setup tests
Fivetran performs the following tests to ensure that we can connect to your Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL database and that it is properly configured:
- The Connecting to SSH Tunnel Test validates the SSH tunnel details you provided in the setup form. It then checks that we can connect to your database using the SSH Tunnel. (We skip this test if you aren't connecting using SSH.)
- The Connecting to Host Test validates the database credentials you provided in the setup form. The test verifies that the host is not private and then checks the connectivity to the host.
- The Validating Certificate Test generates a pop-up window where you must choose which certificate you want Fivetran to use. It then validates that certificate and checks that we can connect to your database using TLS. (We skip this test if you selected an indirect connection method and then disabled the Require TLS through Tunnel toggle.)
- The Connecting to Database Test checks that we can access your database.
- The Connecting to WAL Replication Slot Test confirms that the database associated with the replication slot matches the name you supplied in the setup form. It then verifies that the replication slot uses the
pgoutputplugin. Lastly, it makes sure that the Fivetran user has replication privileges. (We skip this test if you selected Query-Based as your incremental sync method) - The Checking Configuration Values Test checks a set of WAL-configured values against the recommended settings and detects if they are below the recommended range. (We skip this test if you selected Query-Based as your incremental sync method.)
- The Publication Test verifies that the supplied publication name exists in your database. (We skip this test if you selected Query-Based as your incremental sync method.)
- The Query-Based Extensions Test checks that the correct extensions are enabled for the Query-Based incremental sync method. (This test is skipped if you select Logical Replication as your incremental sync method.)
The tests may take a few minutes to finish running.