SQL Server Destination Setup Guide
Follow our setup guide to connect SQL Server database as a destination to Fivetran.
Prerequisites
To connect SQL Server to Fivetran, you need the following:
- SQL Server Version 2012 or above
- IP (for example,
1.2.3.4) or host (your.server.com) - Port (usually
1433) - Access to your SQL Server through Fivetran's IPs for your database's region
- A Fivetran-specific SQL Server user with WRITE-level permissions
- A Fivetran user account with permissions to create or manage destinations
We only support the Enterprise and Standard editions of SQL Server.
Setup instructions
Choose your deployment model
Before setting up your destination, decide which deployment model best suits your organization's requirements. This destination supports both SaaS and Hybrid deployment models, offering flexibility to meet diverse compliance and data governance needs.
See our Deployment Models documentation to understand the use cases of each model and choose the model that aligns with your security and operational requirements.
You must have an Enterprise or Business Critical plan to use the Hybrid Deployment model.
Choose connection method
Decide whether to connect to your SQL Server database directly, using an SSH tunnel, or using private link. For more information, see our destination connection options documentation.
Connect directly
If you connect directly, you must create a rule in a security group that allows Fivetran access to your database instance and port.
Configure your firewall and/or other access control systems to allow incoming connections to your host and port from Fivetran's IPs for your database's region.
Connect using an SSH tunnel
If you connect using an SSH tunnel, Fivetran connects to a separate server in your network that provides an SSH tunnel to your SQL Server database. You must then configure your tunnel server's security group to allow Fivetran access and configure the instance's security to allow access from the tunnel.
You must connect through SSH if your database is contained within an inaccessible subnet.
To connect using SSH, do the following:
In the destination setup form, select the Connect via an SSH tunnel option.
Copy Fivetran's public SSH key.
Add the public key to the
authorized_keysfile of your SSH server. The key must be all on one line, so make sure that you don't introduce any line breaks when cutting and pasting.
Connect using AWS PrivateLink
You must have a Business Critical plan to use AWS PrivateLink.
AWS PrivateLink allows VPCs and AWS-hosted or on-premises services to communicate with one another without exposing traffic to the public internet. PrivateLink is the most secure connection method. Learn more in AWS’ PrivateLink documentation.
Follow our AWS PrivateLink setup guide to configure PrivateLink for your destination.
Connect using Azure Private Link
You must have a Business Critical plan to use Azure Private Link.
Azure Private Link allows Virtual Networks (VNets) and Azure-hosted or on-premises services to communicate with one another without exposing traffic to the public internet. Learn more in Microsoft's Azure Private Link documentation.
Follow our Azure PrivateLink setup guide to configure Private Link for your destination.
Connect using Google Cloud Private Service Connect
Google Cloud Private Service Connect allows VPCs and Google-hosted or on-premises services to communicate with one another without exposing traffic to the public internet. Learn more in Google Cloud's Private Service Connect documentation.
Follow our Google Cloud Private Service Connect setup guide to configure Private Link for your destination.
Connect using Proxy Agent
Fivetran connects to your destination host through the Proxy Agent, providing secure communication between Fivetran processes and your warehouse host. The Proxy Agent is installed in your network and creates an outbound network connection to the Fivetran-managed SaaS.
To learn more about the Proxy Agent, how to install it, and how to configure it, see our Proxy Agent documentation.
Enable TCP/IP
Verify that your SQL Server database is configured to allow TCP/IP connections. To enable the TCP/IP protocol for your database instance:
Open SQL Server Configuration Manager.
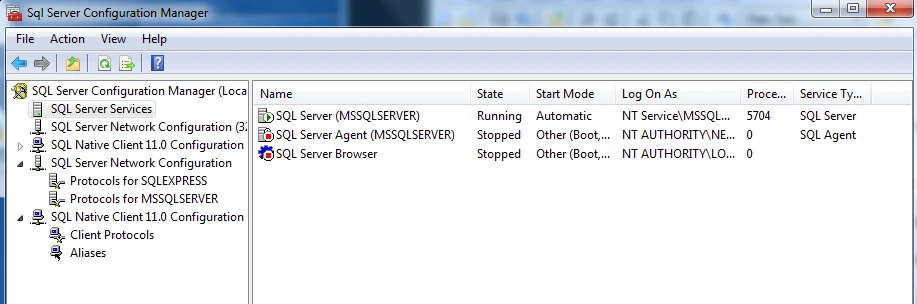
In the navigation pane, click SQL Server Network Configuration, and then click Protocols for MyInstanceName.
If you specified the default instance during installation, the instance name will be MSSQLSERVER.
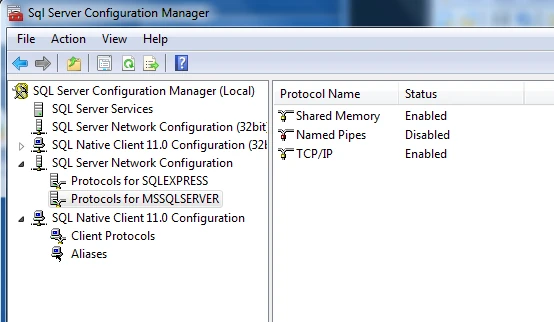
In the right pane, verify that the TCP/IP protocol is Enabled. If the status is Disabled, right-click TCP/IP, and then click Enable.
Right-click TCP/IP and select Properties.
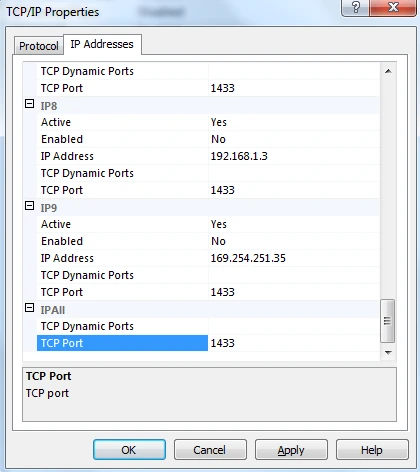
In the IP Addresses tab, go to the IPAll section.
In the TCP Port field enter 1433, and then click Apply.
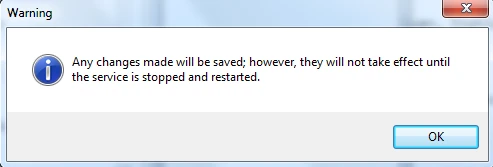
On the warning dialog box, click OK, and then on the TCP/IP Properties dialog box, click OK.
In the navigation pane, expand SQL Native Client Configuration, and then click Client Protocols.
In the right pane, verify that TCP/IP is Enabled. If TCP/IP is Disabled, right-click TCP/IP, and then click Enable.
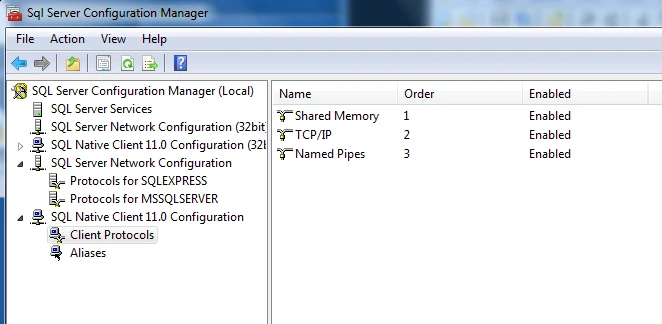
Right-click TCP/IP and select Properties. Verify that the Default Port field is set as 1433 and the Enabled field is set as Yes.
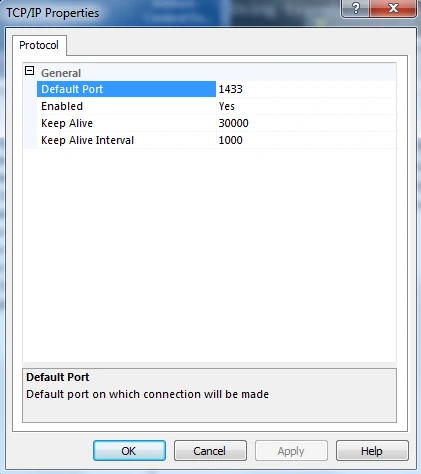
Click OK to exit the TCP/IP Properties dialog box.
In the navigation pane, click SQL Server Services.
In the right pane, right-click SQL Server (MyInstanceName), and then click Restart.
Verify SSL encryption
- Open SQL Server Configuration Manager.
- In the navigation pane, expand SQL Server Network configuration.
- Select Protocols for MyInstanceName Properties.
- In the right pane, go to the Certificate tab and make sure that the encryption certificate is enabled.
See Microsoft's documentation to enable encrypted connections to the database engine, if the certificate is not enabled.
The certificate must be in PFX (.pfx) format. If not, the certificate will not be available in the Microsoft Management Console's All Tasks > Manage Private Keys menu.
Create Fivetran user
Connect to your SQL Server database as an Admin user and execute the following SQL commands to create a user for Fivetran. Choose a memorable username (for example, fivetran). Replace <database> with the name of your database and <password> with a password of your choice:
USE [<database>]; CREATE LOGIN fivetran WITH PASSWORD = '<password>'; CREATE USER fivetran FOR LOGIN fivetran;
Grant permissions
Execute the following commands to grant the fivetran user CREATE permission for the database you would like Fivetran to sync:
GRANT CREATE SCHEMA TO fivetran; GRANT CREATE TABLE TO fivetran;
(Optional) Enable auto-growth option for transaction log
Run the following query to check whether the auto-growth option is already enabled for the transaction log:
SELECT name, growth, max_size FROM sys.database_files where name = '<database_name>_log'Replace
<database_name>in the query with the name of your database.Depending on the query result, do one of the following:
If the result is any value other than
0, it indicates that the auto-growth option is already enabled for the transaction log and you can skip to the next step.If the result is
0, run the following query to enable the auto-growth option:ALTER DATABASE <database_name> MODIFY FILE ( NAME = '<database_name>_log', FILEGROWTH = 1024MB, MAXSIZE = 200GB )You can adjust the
FILEGROWTHandMAXSIZEvalues according to your workload. For more information, see Microsoft documentation.
Complete Fivetran configuration
Log in to your Fivetran account.
Go to the Destinations page and click Add destination.
Enter a Destination name of your choice and then click Add.
Select SQL Server as the destination type.
(Enterprise and Business Critical accounts only) Select the deployment model of your choice:
- SaaS Deployment
- Hybrid Deployment
If you selected Hybrid Deployment, click Select Hybrid Deployment Agent and do one of the following:
- To use an existing agent, select the agent you want to use, and click Use Agent.
- To create a new agent, click Create new agent and follow the setup instructions specific to your container platform.
Enter the Host name or the IP address of the database server.
Enter the Port number. For example,
1433.Enter the User name you created in Step 5.
Enter your Password.
Enter the Database name you want to replicate to.
(Not applicable to Hybrid Deployment) Choose your Connection method:
- Connect directly
- Connect via an SSH
- Connect via PrivateLink
- Connect using Proxy Agent
The Connect via PrivateLink option is available only for Business Critical accounts.
If you choose Connect via an SSH tunnel in the Connection method drop-down menu, enter the following details:
- SSH Host
- SSH Port
- SSH User
- (Optional) If you enabled TLS on your database in Step 2, make sure to keep the Require TLS through Tunnel toggle turned ON.
(Not applicable to Hybrid Deployment) Choose the Data processing location. Depending on the plan you are on and your selected cloud service provider, you may also need to choose a Cloud service provider and cloud region as described in our Destinations documentation.
If you are using AWS PrivateLink, Azure Private Link, or Google Cloud Private Connect Service, select the corresponding Cloud service provider.
Choose your Time zone.
(Optional for Business Critical accounts and SaaS Deployment) To enable regional failover, set the Use Failover toggle to ON, and then select your Failover Location and Failover Region. Make a note of the IP addresses of the secondary region and safelist these addresses in your firewall.
Click Save & Test.
Fivetran tests and validates the SQL Server destination connection. On successful completion of the setup tests, you can sync your data using Fivetran connectors to the SQL Server destination.
In addition, Fivetran automatically configures a Fivetran Platform connection to transfer the connection logs and account metadata to a schema in this destination. The Fivetran Platform Connector enables you to monitor your connections, track your usage, and audit changes. The Fivetran Platform connection sends all these details at the destination level.
If you are an Account Administrator, you can manually add the Fivetran Platform connection on an account level so that it syncs all the metadata and logs for all the destinations in your account to a single destination. If an account-level Fivetran Platform connection is already configured in a destination in your Fivetran account, then we don't add destination-level Fivetran Platform connections to the new destinations you create.
Setup tests
Fivetran performs the following SQL Server connection tests:
The Proxy Agent Status Test checks if the Proxy Agent is running and connected to Fivetran. We skip this test if you are not connecting using a Proxy Agent.
The SSH Tunnel Test validates the SSH tunnel details you provided in the setup form and then checks the connectivity to the instance using the SSH Tunnel if you are connecting using an SSH tunnel.
The Database Host Connection Test validates the database credentials you provided in the setup form. The test verifies that the host is not private and then checks the connectivity to the host.
The Database Certificate Validation Test generates a pop-up window where you must choose which certificate you want Fivetran to use. The test then validates that certificate and checks that we can connect to your database using TLS. We skip this test if you aren't connecting directly.
The SQL Server Connection Test checks if we can access your database.
The Permission Test checks that we have the correct permissions to create schemas and tables in your database.
The SQL Server Type Test validates the SQL Server service type. The test checks if your SQL Server implementation matches the destination type. For example, this test will fail if you try to set up a generic SQL Server destination using an Azure SQL database.
The tests may take a couple of minutes to finish running.