Azure SQL Database Setup Guide
Follow these instructions to replicate your Azure SQL database to your destination via Fivetran.
Prerequisites
To connect your SQL Server database to Fivetran, you need:
- SQL Server version 2012 or above
- An Azure account with a DB Owner, SQL Server Contributor, or SQL Security Manager role
- ALTER ANY USER permissions in your database server
- Your database host's IP (for example,
1.2.3.4) or domain (for example,your.server.com) - Your database's port (usually
1433) - (If you want to connect using SSH) An SSH server
We do not support single-user mode.
Setup instructions
Choose authentication method
Decide on your preferred authentication method and complete the required configuration steps in the Azure Portal and Azure SQL Database.
Authenticate with Microsoft Entra ID OAuth
Microsoft Entra ID allows Fivetran to authenticate using OAuth 2.0 with a secure and centralized identity provider. This method allows you to:
- Avoid sharing usernames or passwords with Fivetran
- Maintain control over access permissions via Azure roles or groups
- Revoke access at any time through the Microsoft Entra ID portal
IMPORTANT:
- You must have a properly configured Microsoft Entra ID tenant within your Azure account.
- Your Azure SQL Database must be configured to support Entra ID authentication.
- Your Azure SQL logical server must have an Active Directory administrator assigned. This role is required to create Entra ID users in the database and enable Fivetran to authenticate using Entra ID.
- Follow Azure’s official guide for setup.
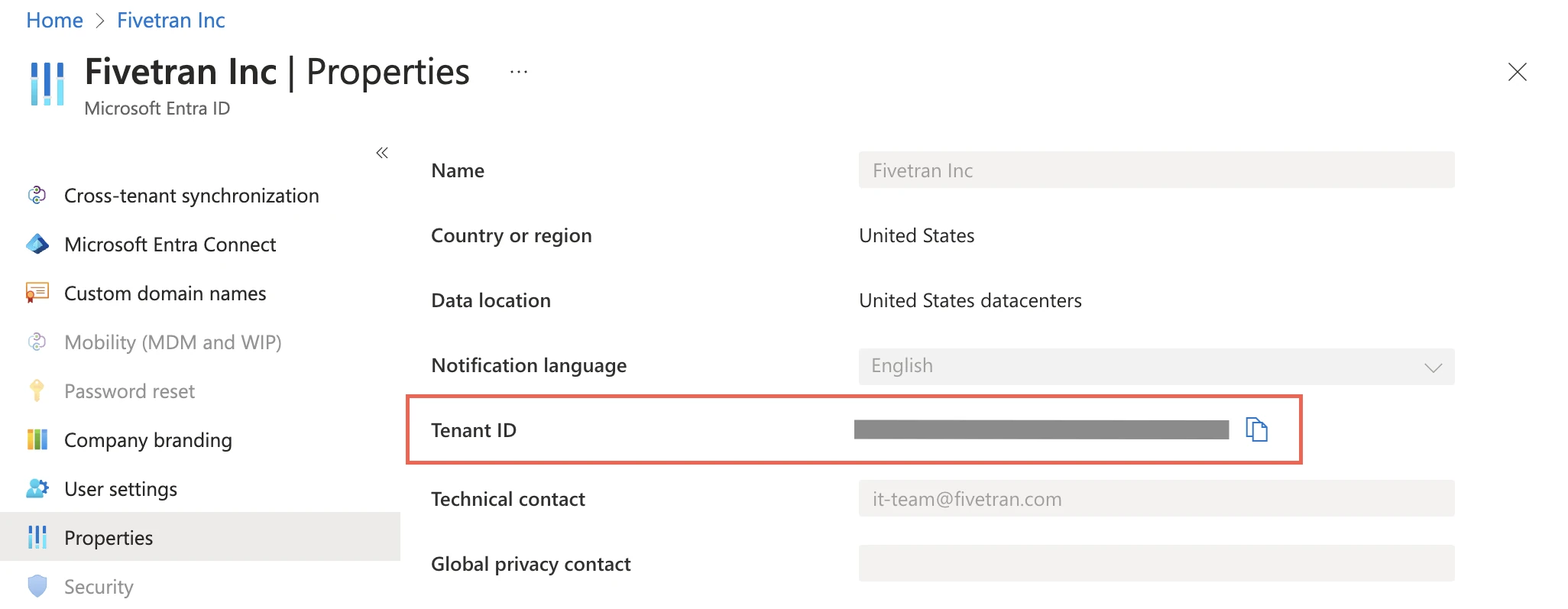
Retrieve your Entra ID Tenant ID
Open the Azure Portal and sign in.
Go to Azure Active Directory.
In the left-hand menu, click Properties.
Copy the value labeled Tenant ID. You will need to enter this in the Fivetran connection setup form later.
Create a user in Azure SQL Database
Even though Fivetran authenticates via OAuth, your database still requires a mapped user to issue queries. The user can be an individual account or a group that has been assigned access.
In your Azure SQL Database, run the following command. Replace <PRINCIPAL-NAME> with either of the following:
The User Principal Name (UPN) of the Entra ID user (for example,
user@yourdomain.com)The Group Principal Name, if the user is a member of an Entra security group authorized to access the database
CREATE USER [<PRINCIPAL-NAME>] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER;You’ll grant the database permissions to this Entra ID user or group in the Grant user permissions step later.
Authenticate with Microsoft Entra ID Managed Identity (only available on Hybrid Deployment)
Microsoft Entra ID Managed Identity allows Fivetran to authenticate securely without using or storing usernames or passwords.
To use this authentication method, your Azure SQL Database must have Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure Active Directory) authentication enabled, and you must be signed in with a user who has the Microsoft Entra admin role on the database.
Additionally, this method is supported only in Hybrid Deployment and requires that both the Hybrid Deployment Agent and the Azure SQL Database reside under the same Microsoft Entra tenant.
Follow Azure’s guide to configuring Entra ID authentication for Azure SQL to enable Entra ID authentication.
Follow Azure’s Managed Identity documentation to enable and assign a Managed Identity to the Azure resource where the Fivetran's Hybrid Deployment Agent runs.
To use this method, you need the following:
- A Managed Identity (either User Assigned or System Assigned) configured on the Azure resource (such as a VM) where the Fivetran Hybrid Deployment Agent is installed.
- The Managed Identity’s Client ID (for User Assigned Managed Identity only)
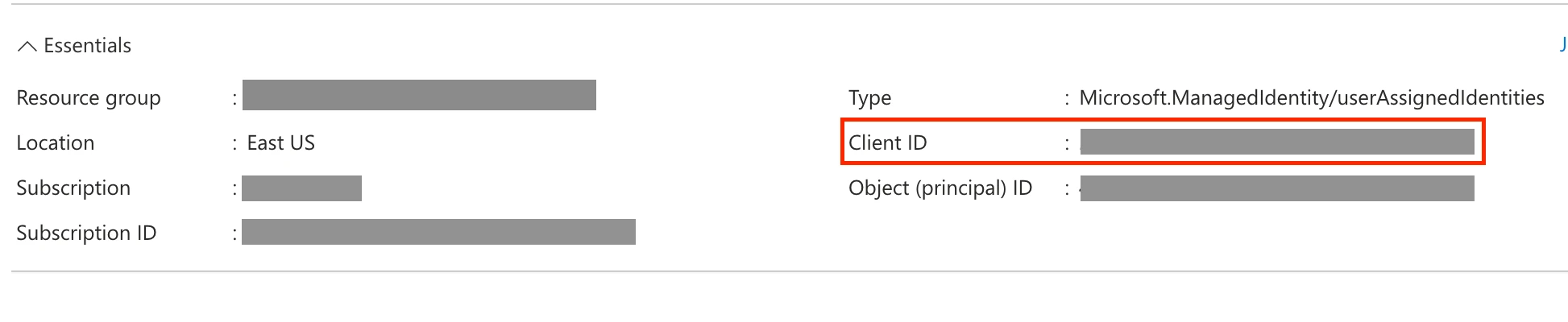
Retrieve the Managed Identity Client ID (User Assigned Managed Identity only)
Open the Azure Portal and sign in.
In the top search bar, search for 'Managed Identities'.
Select the User Assigned Managed Identity you want to use.
In the Overview tab, copy the Client ID. You will need to enter this in the Fivetran connection setup form later.
Create a user in Azure SQL Database
To allow your Managed Identity (UAMI or SAMI) to access the Azure SQL Database, create a user in the database using the following command. Replace <PRINCIPAL-NAME> with the name of your Managed Identity.
CREATE USER [<PRINCIPAL-NAME>] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER;
You’ll grant the appropriate database permissions to this Managed Identity user in the Grant user permissions step later.
Authenticate with Microsoft Entra ID Service Principal with Client Secret
Microsoft Entra ID Service Principal with Client Secret authentication allows Fivetran to connect to your Azure SQL Database using a Service Principal identity registered in your Microsoft Entra ID tenant.
To use this method, you need the following:
- A Service Principal registered in Microsoft Entra ID
- The Service Principal Client ID (Application ID)
- The Service Principal Client Secret
Register a Service Principal in Microsoft Entra ID
- Open the Azure Portal and sign in.
- Navigate to Microsoft Entra ID > App registrations.
- Click + New registration.
- Enter a name for the app (for example,
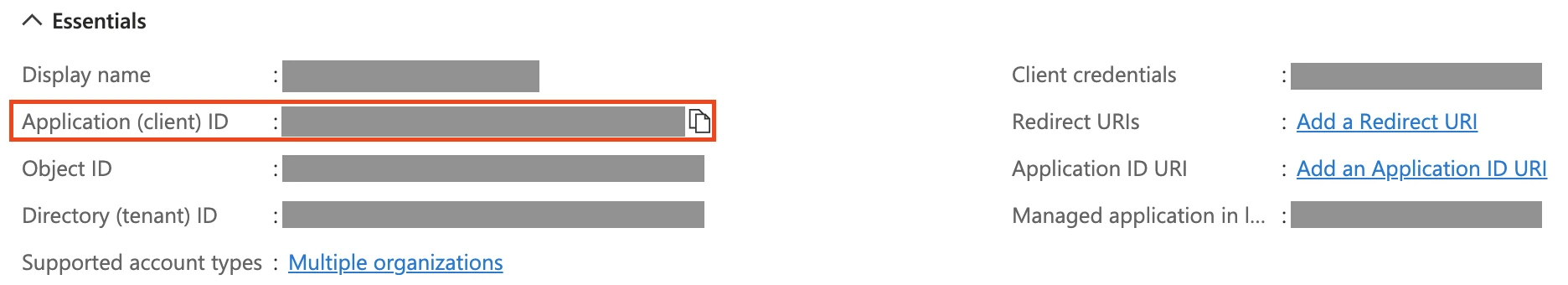
Fivetran-SQL-Connector) and click Register. - Once registered, go to the app’s Overview tab and copy the Application (client) ID. This is your Service Principal Client ID. You will need to enter this in the Fivetran connection setup form later.
Create a Client Secret
In the left-hand menu of your app, go to Certificates & secrets.
Under Client secrets, click + New client secret:
Enter a description and choose an expiration period.
Click Add.
Copy the Value of the secret immediately - it is shown only once.
Keep this secret secure and monitor its expiration to avoid disruptions.
This is your Service Principal Client Secret. You will also need this in the Fivetran connection setup form.
Create a user in Azure SQL Database
To allow your Service Principal to connect to the Azure SQL Database, run the following command. Replace <PRINCIPAL-NAME> with the name of your Service Principal.
CREATE USER [<PRINCIPAL-NAME>] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER;
You’ll grant the appropriate database permissions to this Service Principal user in the Grant user permissions step later.
Authenticate with Microsoft Entra ID Service Principal with Client Certificate
Microsoft Entra ID Service Principal with Client Certificate authentication allows Fivetran to securely connect to your Azure SQL Database using a Service Principal that is authenticated via a client certificate.
To use this method, you need the following:
- A Service Principal registered in Microsoft Entra ID
- The Service Principal Client ID (Application ID)
- A valid client certificate
- The corresponding private key (if stored separately from the certificate).
Register a Service Principal in Microsoft Entra ID
Open the Azure Portal and sign in.
Navigate to Microsoft Entra ID > App registrations.
Click + New registration.
Enter a name for the app (for example,
Fivetran-SQL-Cert-Auth) and click Register.Once registered, go to the app’s Overview tab and copy the Application (client) ID. This is your Service Principal Client ID. You will need to enter this in the Fivetran connection setup form later.

Generate and upload a client certificate
To authenticate using a certificate, your Service Principal must be configured with a valid public certificate.
There are multiple ways to generate a certificate, and you're free to use any method that fits your organization's tooling or security policies. Two commonly used approaches are:
Generate a certificate using OpenSSL
openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout private-key.key -out certificate.crt -days 365 -nodes
Generate a certificate using Azure Key Vault
In Azure Portal, go to Key Vault > Certificates.
Generate or import a certificate in
.pfxformat.Export the certificate and private key if needed:
openssl pkcs12 -in certificate.pfx -clcerts -nokeys -out certificate.crt openssl pkcs12 -in certificate.pfx -nocerts -out private-key.keyAzure Key Vault does not allow downloading the private key for certificates generated inside Key Vault. To retrieve the private key, you must have imported a
.pfxfile during creation.
Regardless of the method you choose, the certificate you upload to the App registration must be in one of the following supported formats: .cer, .crt, or .pem.
After generating the certificate:
- Navigate to your App registration in the Azure Portal.
- Go to Certificates & secrets > Certificates.
- Click Upload certificate, and select a valid
.cer,.crt, or.pemfile.
Create a user in Azure SQL Database
To allow your Service Principal to connect to the Azure SQL Database, run the following command. Replace <PRINCIPAL-NAME> with the name of your Service Principal:
CREATE USER [<PRINCIPAL-NAME>] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER;
You’ll grant the appropriate database permissions to this Service Principal user in the Grant user permissions step later.
Authenticate with username and password
This method allows you to authenticate Fivetran using a username and password for a properly configured user in your Azure SQL Database. You will create this user later in the setup process.
Choose connection method
Next, decide whether to connect your SQL Server database directly, using an SSH tunnel, using Azure Private Link, or using Proxy Agent.
Connect directly (TLS required)
You must have TLS enabled on your database to connect directly to Fivetran. Follow Azure's TLS setup instructions to enable TLS on your database.
Fivetran connects directly to your database instance. This is the simplest connection method.
To connect directly, create a firewall rule to allow access to Fivetran's IPs for your database's region.
Connect using SSH (TLS optional)
Fivetran connects to a separate server in your network that provides an SSH tunnel to your database. You must connect through SSH if your database is in an inaccessible subnet on a virtual network.
You must create a firewall rule to allow access to your SSH tunnel server's IP address.
To connect using SSH, do the following:
In the connection setup form, select Connect via an SSH tunnel as the Connection Method.
Make a note of the Public Key. You will need it to set up your SSH client.
Follow our SSH connection instructions. If you want Fivetran to tunnel SSH over TLS, follow Azure's TLS setup instructions to enable TLS on your database.
Connect using Azure Private Link
You must have a Business Critical plan to use Azure Private Link.
Azure Private Link allows Virtual Networks (VNets) and Azure-hosted or on-premises services to communicate with one another without exposing traffic to the public internet. Learn more in Microsoft's Azure Private Link documentation.
Follow our Azure PrivateLink setup guide to configure Private Link for your database.
Connect using Proxy Agent
Fivetran connects to your database through the Proxy Agent, providing secure communication between Fivetran processes and your database host. The Proxy Agent is installed in your network and creates an outbound network connection to the Fivetran-managed SaaS.
To learn more about the Proxy Agent, how to install it, and how to configure it, see our Proxy Agent documentation.
Enable access
Configure a server firewall to grant Fivetran's data processing servers access to your database.
Log in to the Azure console.
On the Azure main page, select SQL databases.
Click on the SQL database that you want to connect to Fivetran.
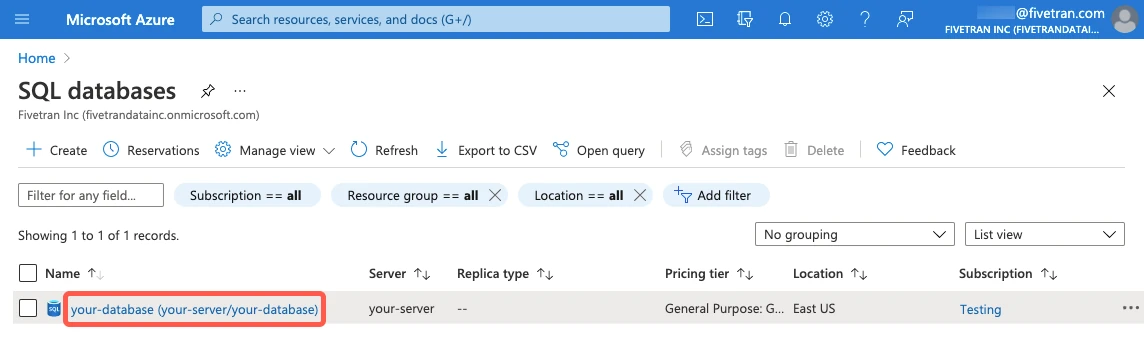
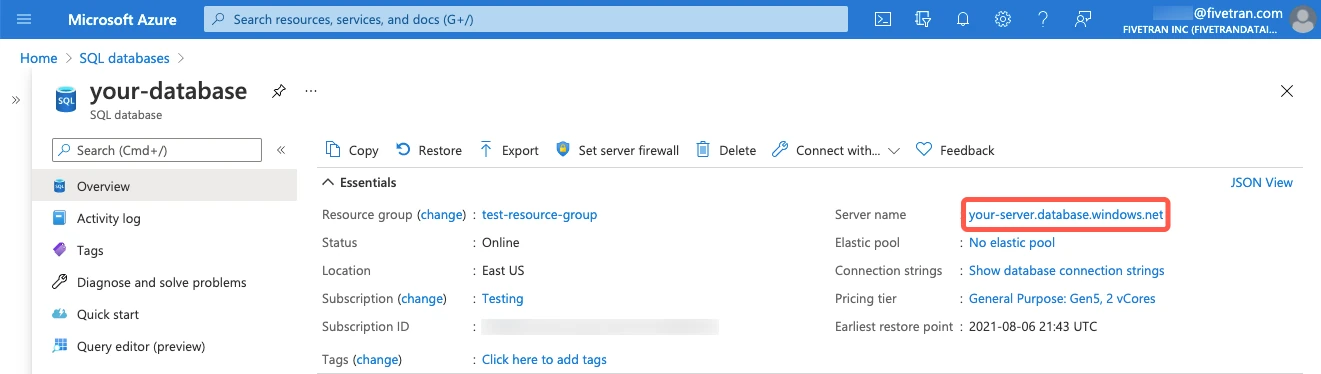
On the database overview page, find the server name and make a note of it. You will need it to configure Fivetran.
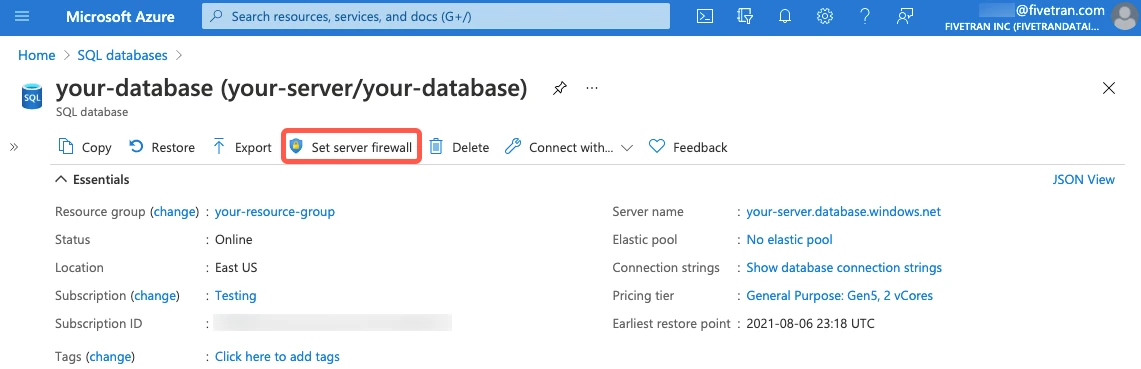
Click Set server firewall.
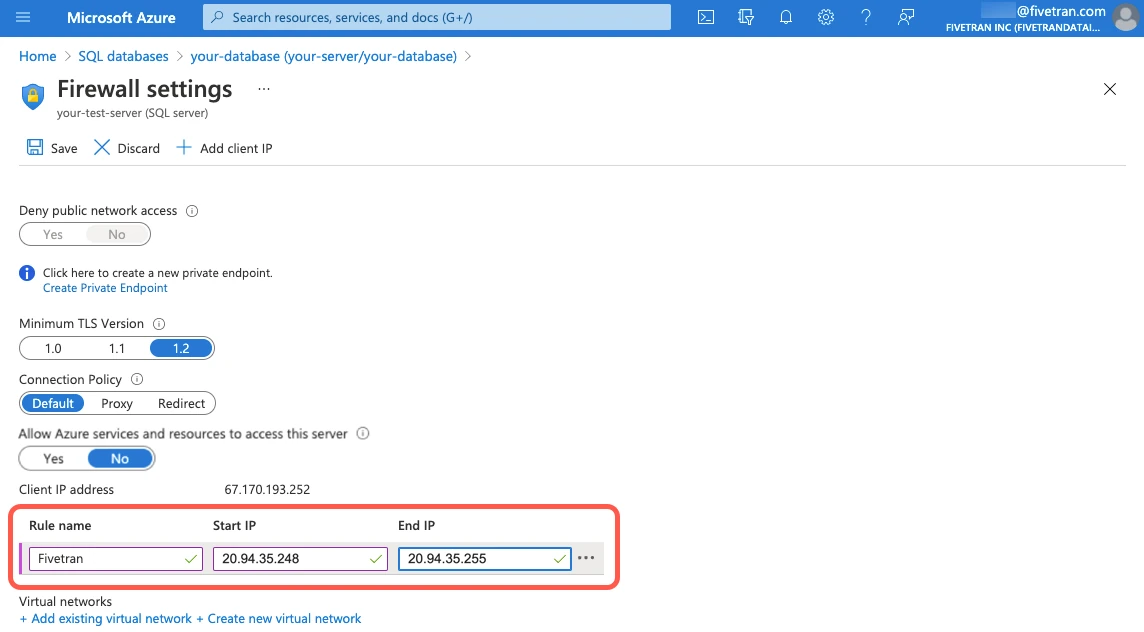
On the Firewall settings page, add a new firewall rule with a memorable name (for example,
Fivetran). What you enter in the IP fields depends on whether you're connecting directly or using an SSH tunnel.- If you're connecting directly, enter Fivetran's IPs for your database's region.
- If you're connecting using an SSH tunnel, enter your SSH tunnel server's IP address and set the Connection Policy to Proxy.
Click Save.
Create user
If you're authenticating Fivetran with a username and password, create a database user for Fivetran's exclusive use.
If you are authenticating with Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure Active Directory), skip ahead to Grant user permissions.
Open a connection to your Azure SQL database.
Add a container database user for Fivetran by running the following command. Replace
<database>with the name of your database,<username>with the username of your choice, and<password>with a password of your choice:USE [<database>]; CREATE USER <username> WITH PASSWORD = '<password>';
Grant user permissions
Once you've created the Fivetran user, grant it SELECT permission for the database, schemas, tables, or specific columns you want Fivetran to sync. You can grant access to everything in a given database:
GRANT SELECT on DATABASE::[<database>] to [<username>];or all tables in a given schema:
GRANT SELECT on SCHEMA::[<schema>] to [<username>];or a specific table:
GRANT SELECT ON [<schema>].[<table>] TO [<username>];or a set of specific columns in a table:
GRANT SELECT ON [<schema>].[<table>] ([<column 1>], [<column 2>], ...) TO [<username>];or all but a set of specific columns in a table:
GRANT SELECT ON [<schema>].[<table>] TO <username>; DENY SELECT ON [<schema>].[<table>] ([<column X>], [<column Y>], ...) TO [<username>];or add a managed database-level role:
ALTER ROLE <role-name> add member [<username>];(Optional) For SQL Server for Linux, if you are using Change Tracking with history mode enabled, to improve performance and reduce delays, you may want to grant the necessary permissions to the Fivetran user by running the following command:
USE [master]; GRANT VIEW SERVER STATE TO <username>;This grants the Fivetran user access to server state information, minimizing the dependency on checkpoint timing and reducing update delays. See the Sync Delays with SQL Server for Linux Using Change Tracking with History Mode Enabled troubleshooting page for details.
Enable incremental updates
For incremental updates, we use one of the following tracking mechanisms:
These mechanisms let Fivetran copy only the rows that have changed since the last data sync so we don't have to copy the whole table every time. Learn more in our updating data documentation.
Choose to enable change tracking, change data capture, or Fivetran Teleport Sync.
Change tracking
Expand for instructions
Enable change tracking at the database level:
ALTER DATABASE [<database>] SET CHANGE_TRACKING = ON (CHANGE_RETENTION = 7 DAYS, AUTO_CLEANUP = ON);While we recommend seven days of change retention, you can set your retention period as low as one day. However, a shorter retention period increases the risk that your logs will expire in between syncs, triggering an automatic full source re-sync.
Enable CT for each table you want to integrate:
ALTER TABLE [<schema>].[<table>] ENABLE CHANGE_TRACKING;Grant the Fivetran user
VIEW CHANGE TRACKINGpermission for each of the tables that have change tracking enabled:GRANT VIEW CHANGE TRACKING ON [<schema>].[<table>] TO <username>;
Change data capture
Expand for instructions
Enable change data capture at the database level:
USE TEST; EXEC sys.sp_cdc_enable_db;Enable CDC for each table you want to integrate:
EXEC sys.sp_cdc_enable_table @source_schema = [<schema>], @source_name = [<table>], @role_name = [<username>], @supports_net_changes = 0;Fivetran only supports tables with a single CDC capture instance. Our syncs only include tables and columns that are present in a CDC instance. If you add new tables or columns, you must create a new CDC instance that includes them and delete the old instance.
When @supports_net_changes is set to 1, an additional non-clustered index is created on the change table. Because this index needs to be maintained, enabling net changes can degrade CDC performance.
Set your CDC retention period:
EXEC sys.sp_cdc_change_job @job_type = N'cleanup', @retention = 10080; -- Sets the retention period to 7 daysWhile we recommend seven days of change retention, you can set your retention period as low as one day. However, a shorter retention period increases the risk that your logs will expire in between syncs, triggering an automatic full source re-sync.
Fivetran Teleport Sync
You do not need to do any additional configuration to use Fivetran Teleport Sync.
(Optional) Schema changes for change tracking (CT) and change data capture (CDC) Beta
By default, when you create a new table in your database, you must manually enable CT or CDC for that table before we can sync it. Additionally, if you add a new column to an existing CDC-enabled table, you must manually recreate the CDC capture instance before we can sync the column.
If you want Fivetran to automatically enable CT or CDC for newly created tables and to update CDC capture instances when a new column is added, install the following stored procedures on your database. If your connector contains only CT-enabled tables, then any subsequent new tables will be CT-enabled. If your connector has a mixture of CT- and CDC-enabled tables or contains CDC-enabled tables only, then we will enable CDC over CT by default.
Expand for instructions
Install the following script on your database. Before running the script, replace
<database>with your database name.If you have configured your connector to "Allow columns", you can exclude the
[dbo].[sp_ft_enable_cdc]and[dbo].[sp_ft_enable_change_tracking]stored procedures. If you have configured your connector to "Block All", you can exclude all the following stored procedures.USE [<database>]; /****** Object: StoredProcedure [dbo].[sp_ft_enable_cdc] Script Date: 1/17/2024 11:12:55 PM ******/ SET ANSI_NULLS ON GO SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON GO CREATE OR ALTER PROCEDURE [dbo].[sp_ft_enable_cdc] @TableList NVARCHAR(MAX), @FivetranUser NVARCHAR(MAX) WITH EXECUTE AS OWNER -- Change to an appropriate sysadmin user AS BEGIN SET NOCOUNT ON; -- Table to store tables with results CREATE TABLE #ResultTables (TableName NVARCHAR(MAX), Result NVARCHAR(MAX)); -- Enable CDC for each table DECLARE @TableName NVARCHAR(MAX); DECLARE @SqlStatement NVARCHAR(MAX); WHILE LEN(@TableList) > 0 BEGIN -- Get the first table in the list SET @TableName = NULL; SET @TableName = SUBSTRING(@TableList, 1, CHARINDEX(',', @TableList + ',') - 1); -- Remove the processed table from the list SET @TableList = STUFF(@TableList, 1, LEN(@TableName) + 1, ''); -- Build and execute the SQL statement to enable CDC for the table SET @SqlStatement = ' BEGIN TRY EXEC sys.sp_cdc_enable_table @source_schema = ''' + PARSENAME(@TableName, 2) + ''', @source_name = ''' + PARSENAME(@TableName, 1) + ''', @role_name = ''' + @FivetranUser + ''', @supports_net_changes = 0; INSERT INTO #ResultTables (TableName, Result) VALUES (''' + @TableName + ''', ''Success''); END TRY BEGIN CATCH PRINT ERROR_MESSAGE(); INSERT INTO #ResultTables (TableName, Result) VALUES (''' + @TableName + ''', ERROR_MESSAGE()); END CATCH '; -- Execute the dynamic SQL statement EXEC sp_executesql @SqlStatement; END -- Return the list of tables with results SELECT * FROM #ResultTables; -- Drop the temporary table DROP TABLE #ResultTables; END; GO /****** Object: StoredProcedure [dbo].[sp_ft_enable_change_tracking] Script Date: 1/17/2024 11:10:45 PM ******/ SET ANSI_NULLS ON GO SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON GO CREATE OR ALTER PROCEDURE [dbo].[sp_ft_enable_change_tracking] @TableList NVARCHAR(MAX), @FivetranUser NVARCHAR(MAX) WITH EXECUTE AS OWNER -- Change to an appropriate sysadmin user AS BEGIN SET NOCOUNT ON; -- Table to store tables with results CREATE TABLE #ResultTables (TableName NVARCHAR(MAX), Result NVARCHAR(MAX)); -- Enable change tracking for each table DECLARE @TableName NVARCHAR(MAX); DECLARE @SqlStatement NVARCHAR(MAX); WHILE LEN(@TableList) > 0 BEGIN -- Get the first table in the list SET @TableName = NULL; SET @TableName = SUBSTRING(@TableList, 1, CHARINDEX(',', @TableList + ',') - 1); -- Remove the processed table from the list SET @TableList = STUFF(@TableList, 1, LEN(@TableName) + 1, ''); -- Build and execute the SQL statement to enable change tracking SET @SqlStatement = ' BEGIN TRY ALTER TABLE ' + @TableName + ' ENABLE CHANGE_TRACKING; GRANT VIEW CHANGE TRACKING ON ' + @TableName + ' TO ' + @FivetranUser + '; INSERT INTO #ResultTables (TableName, Result) VALUES (''' + @TableName + ''', ''Success''); END TRY BEGIN CATCH PRINT ERROR_MESSAGE(); INSERT INTO #ResultTables (TableName, Result) VALUES (''' + @TableName + ''', ERROR_MESSAGE()); END CATCH '; -- Execute the dynamic SQL statement EXEC sp_executesql @SqlStatement; END -- Return the list of tables with results SELECT * FROM #ResultTables; -- Drop the temporary table DROP TABLE #ResultTables; END; GO /****** Object: StoredProcedure [dbo].[sp_ft_get_tables_with_ddl_changes] Script Date: 1/30/2024 9:10:47 PM ******/ SET ANSI_NULLS ON GO SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON GO CREATE OR ALTER PROCEDURE [dbo].[sp_ft_get_tables_with_ddl_changes] @TableList NVARCHAR(MAX), @ddlTime DATETIME = NULL -- New parameter for ddlTime WITH EXECUTE AS OWNER -- Change to an appropriate sysadmin user AS BEGIN SET NOCOUNT ON; -- Declare a table variable to store the results DECLARE @ChangedTables TABLE ( TableName NVARCHAR(MAX), DdlTime DATETIME ); -- Split the comma-separated list into a table variable DECLARE @TableNames TABLE ( TableName NVARCHAR(MAX) ); INSERT INTO @TableNames (TableName) SELECT value FROM STRING_SPLIT(@TableList, ','); -- Check for DDL changes in cdc.ddl_history INSERT INTO @ChangedTables (TableName, DdlTime) SELECT tn.TableName, MAX(dh.ddl_time) AS LatestDdlTime FROM cdc.ddl_history dh INNER JOIN @TableNames tn ON CONCAT(OBJECT_SCHEMA_NAME(dh.source_object_id), '.', OBJECT_NAME(dh.source_object_id)) = tn.TableName WHERE @ddlTime IS NULL OR dh.ddl_time >= @ddlTime GROUP BY tn.TableName; -- Return the list of tables with the latest DDL changes SELECT TableName, DdlTime FROM @ChangedTables; END; GO /****** Object: StoredProcedure [dbo].[sp_ft_update_cdc] Script Date: 1/31/2024 1:19:40 AM ******/ SET ANSI_NULLS ON GO SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON GO CREATE OR ALTER PROCEDURE [dbo].[sp_ft_update_cdc] @TableName NVARCHAR(MAX), @FivetranUser NVARCHAR(MAX), @CaptureInstance NVARCHAR(MAX), @CapturedColumnList NVARCHAR(MAX) WITH EXECUTE AS OWNER AS BEGIN SET NOCOUNT ON; -- Table to store tables with results CREATE TABLE #ResultTables (TableName NVARCHAR(MAX), Result NVARCHAR(MAX)); DECLARE @SourceSchema NVARCHAR(MAX); DECLARE @SourceName NVARCHAR(MAX); BEGIN TRY -- Assign values to variables for PARSENAME function SET @SourceSchema = PARSENAME(@TableName, 2); SET @SourceName = PARSENAME(@TableName, 1); -- Step 1: Disable the current CDC instance EXEC sys.sp_cdc_disable_table @source_schema = @SourceSchema, @source_name = @SourceName, @capture_instance = @CaptureInstance; -- Step 2: Create a new CDC instance EXEC sys.sp_cdc_enable_table @source_schema = @SourceSchema, @source_name = @SourceName, @role_name = @FivetranUser, @capture_instance = @CaptureInstance, @captured_column_list = @CapturedColumnList, @supports_net_changes = 0; -- Insert the result into the #ResultTables table INSERT INTO #ResultTables (TableName, Result) VALUES (@TableName, 'Success'); END TRY BEGIN CATCH PRINT ERROR_MESSAGE(); -- Insert the error message into the #ResultTables table INSERT INTO #ResultTables (TableName, Result) VALUES (@TableName, ERROR_MESSAGE()); END CATCH; -- Return the list of tables with results SELECT * FROM #ResultTables; -- Drop the temporary table DROP TABLE #ResultTables; END; GOGrant the Fivetran user execute permission.
USE [<database>]; GRANT EXECUTE ON dbo.sp_ft_enable_cdc to <username>; GRANT EXECUTE ON dbo.sp_ft_enable_change_tracking to <username>; GRANT EXECUTE ON dbo.sp_ft_get_tables_with_ddl_changes to <username>; GRANT EXECUTE ON dbo.sp_ft_update_cdc to <username>;
Finish Fivetran configuration
In your connection setup form, enter a Destination schema prefix. This is used as the connection name and cannot be modified once the connection is created.
In the Destination schema names field, choose the naming convention you want Fivetran to use for the schemas, tables, and columns in your destination:
- Source naming: Preserves the original schema, table, and column names from the source system in your destination.
- Fivetran naming: Standardizes the schema, table, and column names in your destination according to the Fivetran naming conventions.
If you want to modify your selection, make sure you do it before you start the initial sync.
Depending on your selection, we will either prefix the connection name to each replicated schema or use the source schema names instead.
In the Host field, enter your database host's IP (for example,
1.2.3.4) or domain (for example,your.server.com).Enter your database instance's port number. The port number is usually
1433.For the Database, enter the name of the database you want to connect to Fivetran.
Choose your Authentication Method from the options available in the drop-down. Based on your selection, complete the following fields:
Microsoft Entra ID OAuth (default)
In the Tenant ID field, enter your Microsoft Entra ID tenant ID you found in Step 1.
Click Authorize to start the OAuth sign-in process. You will be redirected to the Microsoft Entra ID sign-in and consent page. After granting consent, you will be redirected back to the Fivetran connection setup form, and the authorization will be saved automatically.
Microsoft Entra ID Managed Identity (only available on Hybrid Deployment)
If you are using a User Assigned Managed Identity, enter the Client ID you found in Step 1 in the User Assigned Managed Identity (optional) field.
If you are using a System Assigned Managed Identity, leave the User Assigned Managed Identity (optional) field blank.
Microsoft Entra ID Service Principal + Client Secret
Microsoft Entra ID Service Principal + Client Certificate
In the Client ID field, enter the Service Principal Client ID you found in Step 1.
In the Client Certificate field, upload the client certificate you prepared in Step 1.
(Optional) In the Private Key for Client Certificate (optional) field, upload the private key file from Step 1 if it is stored separately from the certificate.
(Hybrid Deployment only) If your destination is configured for Hybrid Deployment, the Hybrid Deployment Agent associated with your destination is pre-selected for the connection. To assign a different agent, click Replace agent, select the agent you want to use, and click Use Agent.
(Not applicable to Hybrid Deployment) Choose your connection method. If you selected Connect via an SSH tunnel, copy or make a note of the Public Key and add it to the
authorized_keysfile while configuring the SSH tunnel, and provide the following information:- SSH hostname (do not use a load balancer's IP address/hostname)
- SSH port
- SSH user
- If you enabled TLS on your database in Step 2, make sure to keep the Require TLS through Tunnel toggle turned ON.
Choose your incremental Update Method.
Click Save & Test. Fivetran tests and validates our connection to your Azure SQL database. Upon successful completion of the setup tests, you can sync your data using Fivetran.
Setup tests
Fivetran performs the following tests to ensure that we can connect to your Azure SQL database and that it is properly configured:
- The Connecting to SSH Tunnel Test validates the SSH tunnel details you provided in the setup form. It then checks that we can connect to your database using the SSH Tunnel. (We skip this test if you aren't connecting using SSH.)
- The Connecting to Host Test validates the database credentials you provided in the setup form. It then verifies that the database host is not private and checks that we can connect to the host.
- The Validating Certificate Test generates a pop-up window where you must choose which certificate you want Fivetran to use. It then validates that certificate and checks that we can connect to your database using TLS. (We skip this test if you selected an indirect connection method and then disabled the Require TLS through Tunnel toggle.)
- The Connecting to Database Test checks that we can access your database.
- The Validating Replication Config Test verifies that your database has an incremental sync method enabled (either CDC or CT).
The tests may take a few minutes to finish running.