Reverse SSH
You can connect Fivetran to your destination using a reverse SSH tunnel if you are unable to provide direct port access to your instance. Reverse SSH tunneling allows you to securely connect to a device located behind a firewall or NAT (Network Address Translation) remotely. With this method, the remote machine initiates the connection to the local machine, enabling remote access to services on the local machine.
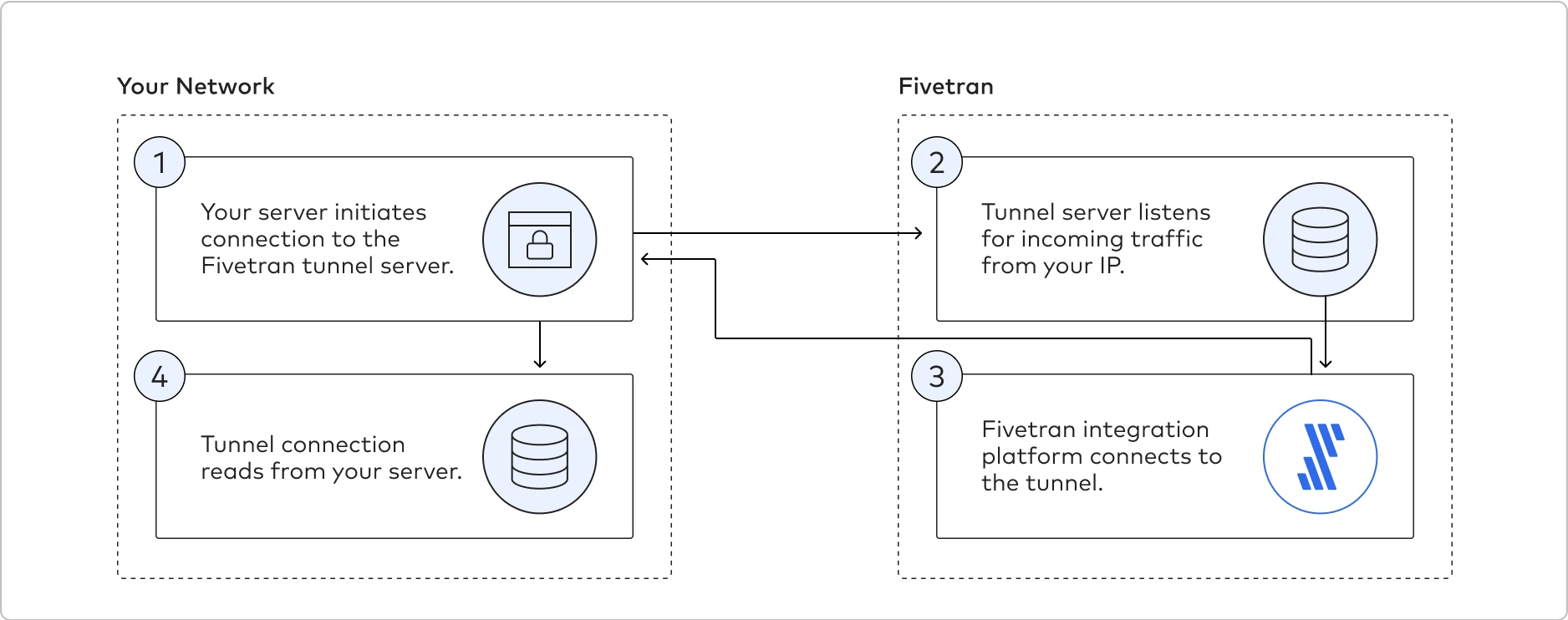
To set up a reverse SSH tunnel to connect to Fivetran, create a Fivetran support ticket and provide the following details:
- Your SSH public key (see instructions below to learn how to generate)
- The public IP address (CIDR notation) of your SSH bastion host or proxy server
Follow the reverse SSH tunnel setup instructions specific to your operating system.
Linux
Expand for instructions
Perform the following steps to set up the reverse SSH tunnel on Linux:
Create an SSH user and generate key pair
Log in to your SSH tunnel host and run the following commands:
Create group
fivetran:sudo groupadd fivetranCreate user
fivetran:sudo useradd -m -g fivetran fivetranSwitch to the
fivetranuser:sudo su - fivetranCreate the
.sshdirectory:mkdir ~/.sshSet permissions:
chmod 700 ~/.sshGenerate an SSH key pair. Make a note of the key path - you will need it to complete your setup.
ssh-keygenDo not enter a password for the key file. When prompted to provide a password, hit Enter instead.
View the contents of the public key.
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pubSend the public key along with the SSH server's IP address and SSH username (
fivetran) to Fivetran Support.
Once we create the Reverse SSH host and complete the setup on our side, we will provide you with the Reverse SSH host IP address and username. Then, proceed to the next step to initiate the SSH connection between your SSH server and Fivetran's Reverse SSH host.
Initiate SSH connection
To set up a secure tunnel between your destination and Fivetran's server, run the autossh command on your SSH server.
autossh -M 0 -f -N -R <SSH_HIGH_PORT>:<LOCAL_DB_MACHINE_NAME_OR_IP>:<LOCAL_DB_MACHINE_PORT> <FIVETRAN_SSH_USERNAME>@<FIVETRAN_SUPPLIED_IP> -g -i <PATH_TO_PRIVATE_KEY> -o ServerAliveInterval=10 -o ServerAliveCountMax=1 -o ExitOnForwardFailure=yes
Replace the placeholder variables with the actual values:
SSH_HIGH_PORT: It should be unique for each connection and should not be a reserved port number (for instance, port22is reserved for SSH connections and port443is reserved for HTTPS).LOCAL_DB_MACHINE_NAME_OR_IP: Internal IP address or name of the local destination host machine.LOCAL_DB_MACHINE_PORT: Internal port for communication with the destination host.FIVETRAN_SSH_USERNAME: SSH username for Fivetran's Reverse SSH host. Contact Fivetran Support for the SSH username.FIVETRAN_SUPPLIED_IP: Reverse SSH host IP address provided by Fivetran (contact Fivetran Support or your Fivetran Technical Team to get this).PATH_TO_PRIVATE_KEY: File path to the private key on the SSH host machine (usuallyid_rsa.pemor simplyid_rsa).
To track the progress of this script, remove the -f flag and add the -v flag to enable verbose logging. Without the flag, you will not see confirmation when the script finishes running successfully.
If you use this autossh script again later for the same SSH high port, you need to terminate your original autossh script before proceeding.
Enter values into destination setup form
Once the reverse SSH tunnel is successfully established, enter the following values in Fivetran's destination setup form:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Host | localhost | Allows your SSH host to handle port routing |
| Port | { SSH high port } | The port that your SSH host will translate (for example, 13306) |
| User | { Destination user } | |
| Password | { Destination user's password } | |
| Database | { Database name } | The database name you want to replicate to |
| Connection Method | Connect using SSH Tunnel | |
| SSH Host | { IP Address } | Supplied by Fivetran |
| SSH Port | 22 | |
| SSH User | fivetran |
PuTTY
Expand for instructions
Start a new PuTTY session.
Configure your session.
- Host Name: Enter the Fivetran server
- Port: 22
Go to Connection > Data, then enter
fivetranas the tunnel username.In the left menu, go to Connection > SSH.
Select the Don’t start a shell or command at all checkbox.
Go to Connection > SSH > Auth.
Click Browse to find your PPK private key.
Under Auth, go to TTY.
Select the Don’t allocate a pseudo terminal checkbox.
Go to Connection > SSH > Tunnel.
In the Source port field, enter the connection port assigned to your connection (for example,
53359).In the hostname:port field, enter your destination's host and port (for example,
127.0.0.1:5432).Make sure that Remote is selected.
Click Add.
To save the connection, click Session in the left menu.
In the Saved Sessions section, enter a name for your stored session, then click Save.
Double-click the session name to initiate the connection.