Capture From SQL Server Using Direct Transaction Log Access
In this capture method (Capture_Method=DIRECT), Fivetran HVR reads transaction log records directly from the DBMS log file using the file I/O. This method is very fast in capturing changes from the SQL Server database. HVR uses this capture method to capture changes from the SQL Server's current and backup transaction log files, as well as compressed backup transaction log files.
The benefits of the Direct Transaction Log Access capture method are:
- It is faster and less resource-intensive when capturing changes from database locations, especially for highly loaded databases. To ensure uninterrupted, low-latency CDC, capture must be running faster than the database is writing the logs. The Direct Transaction Log Access method and pipelined execution ensures optimum efficiency to keep up with the database log writers. As a result, when capture runs continuously, it will be capturing from the tail end of the log where the log writer(s) are writing.
- It supports capture from SQL Server Always On AG secondary database.
To capture using the Direct Transaction Log Access method, the following are required:
- The database account must have SysAdmin or DbOwner or Minimal permissions. For versions up to 6.1.0/12, only SysAdmin permission model is supported.
- The HVR remote agent must be installed on the SQL Server source database server.
- On Linux, the HVR operating system User must have read access to the .ldf files. For this, the User should typically be added to the operating system user group mssql.
- On Windows, the HVR Agent Listener service must run either:
as the same Windows user that the source SQL Server service runs, or
as other Windows user (e.g. HVR database User), which must have Debug programs (SeDebugPrivilege) policy enabled. For more information about Debug programs security policy, refer to the Microsoft documentation.
Click here for the steps to enable/grant Debug programs policy
User account policies can be managed using the Windows Local Security Policy console (accessible from Control Panel ▶ Administrative Tools). The shortcut command to access this console is secpol.msc.
- In the Local Security Policy window, expand Local Policies and click User Rights Assignment.
- Double-click Debug Programs policy available in the list of policies.
- In the Debug programs Properties dialog, click Add User or Group; displays the Select Users, Computers, Accounts, or Groups dialog.
- In the Enter the object names to select field, enter the user account name to whom you want to enable this policy, and click OK.
- Click OK.
By default, members of the Administrators group have this right enabled.
Capturing from SQL Server TDE
Since v6.1.0/10
HVR supports capturing data from SQL Server’s active transaction log files and transaction log backup files encrypted using Transparent Data Encryption (TDE). It also supports capturing from transaction log backup files encrypted using native SQL Server encryption. For more information about TDE, see SQL Server documentation.
HVR supports capturing from log files encrypted with a Database Encryption Key (DEK) protected by either a local certificate or an asymmetric key stored in Azure Key Vault (AKV):
For more information about these key management methods, see SQL Server documentation.
When the certificate or key protecting the DEK is changed, you must add the new certificate or key to the location properties. HVR requires both the old and new certificates or keys to read the logs at the update point. However, no action is required when only the DEK changes, i.e, when a new DEK is generated but the same certificate or key continues to protect both the old and new DEKs. HVR automatically handles this change.
TDE with Local Certificates
In this method, the DEK that encrypts the log files is protected by a local certificate. To capture from these encrypted log files, you must provide the certificate and private key to HVR.
HVR supports capture from log files where the DEK is protected by certificates.
Until HVR 6.2.5/10, the Direct and Archive Only capture methods do not support capturing changes from log files whose DEK is protected by an asymmetric key. However, you can use the SQL Access method to capture changes from these log files, unless the Archive_Log_Path and Archive_Log_Format properties are defined. If these location properties are defined, the same limitation applies to the SQL Access method.
You can configure HVR to capture from TDE-encrypted log files using either of the following interfaces:
Instructions for HVR UI
Since v6.1.0/32
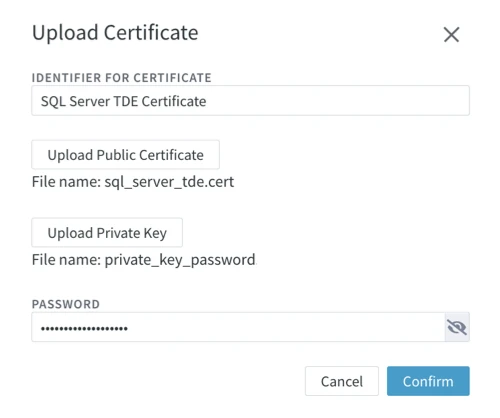
To add a TDE certificate, use the Upload Certificate dialog either when creating a new SQL Server location (Step 4 - Configure Capture/Integrate for SQL Server Location) or when editing source and target properties of an existing SQL Server location.
When creating a new SQL Server location, add the TDE certificate as follows:
- In step 4 - Configure Capture/Integrate for SQL Server Location, select TDE Certificates.
- Click Add Certificate.
- In the Upload Certificate dialog, enter the required certificate information:
- In IDENTIFIER FOR CERTIFICATE, enter a label that uniquely identifies this certificate.
- Upload the Public Certificate and Private Key.
- In Password, enter the password of the private key.
- Click Confirm.
Instructions for CLI
To add a TDE certificate, use the hvrlocationconfig command.
The following are the location properties that you must define to enable capturing from TDE with local certificates:
- SqlServer_TDE_Database_Certificates
- SqlServer_TDE_Database_Private_Keys
- SqlServer_TDE_Database_Private_Key_Passwords.
For example, the following command adds a certificate (cert1), where dbcert.crt and dbcert.pvk are the certificate and private key files (or paths to files), respectively.
hvrlocationconfig hub_name loc_name "SqlServer_TDE_Database_Certificates.cert1=@dbcert.crt" "SqlServer_TDE_Database_Private_Keys.cert1=@dbcert.pvk" "SqlServer_TDE_Database_Private_Key_Passwords.cert1=Passwd1"
Instructions for REST API
To add a TDE certificate, use the REST API endpoint for modifying location properties.
The following are the location properties that you must define to enable capturing from TDE with local certificates -
- SqlServer_TDE_Database_Certificates
- SqlServer_TDE_Database_Private_Keys
- SqlServer_TDE_Database_Private_Key_Passwords.
For example, the following request body adds a certificate (cert1), where dbcert.crt and dbcert.pvk are the certificate and private key files, respectively.
{ "loc_prop_args": [ { "key": ["SqlServer_TDE_Database_Certificates", "cert1"], "value": "" }, { "key": ["SqlServer_TDE_Database_Private_Keys", "cert1"], "value": " " }, { "key": ["SqlServer_TDE_Database_Private_Key_Passwords", "cert1"], "value": "Passwd1" } ] }
TDE with Azure Key Vault
Since v6.2.5/10
In this method, the DEK that encrypts the log files is protected by an asymmetric key stored in Azure Key Vault (AKV). To capture from these encrypted log files, you must provide the AKV URL, key name, and authentication details to HVR. You don't need to upload certificates or private keys to HVR; SQL Server decrypts the DEK using AKV.
For more information about setting up TDE with Azure Key Vault in SQL Server, see the SQL Server documentation.
You can configure HVR to capture from TDE-encrypted log files using either of the following interfaces:
Instructions for UI
To add an AKV configuration, use the Add Azure Key Vault configuration dialog either when creating a new SQL Server location (Step 4 - Configure Capture/Integrate for SQL Server Location) or when editing source and target properties of an existing SQL Server location.
When creating a new SQL Server location, add the AKV configuration as follows:
- In step 4 - Configure Capture/Integrate for SQL Server Location, select TDE Azure Key Vault.
- Click Add Azure Key Vault Configuration.
- In the Add Azure Key Vault Configuration dialog, enter the required configuration details:
- In CONFIGURATION NAME, enter a label that uniquely identifies this configuration (e.g., akv1).
- In VAULT URL, enter the URL (Vault URI) to access the secure secrets, keys, and certificates stored within AKV (https://your-unique-keyvault-name.vault.azure.net/).
- In KEY NAME, enter the versioned AKV key name in the format
KeyName/UUID(e.g., mykey/8f4c79c7e6714a). - Enter the details for your authentication method:
For Managed Identity authentication -
- Select USE MANAGED IDENTITY.
- (Optional) In MANAGED IDENTITY CLIENT ID, enter the client ID of the managed identity.
For Service Principal with a Secret authentication -
- In TENANT ID, enter the tenant ID of the Microsoft Entra ID service principal.
- In CLIENT ID, enter the client ID of the Microsoft Entra ID service principal.
- In CLIENT SECRET, enter the client secret of the Microsoft Entra ID service principal.
- Click Add Configuration.
Instructions for CLI
To add an AKV configuration, use the hvrlocationconfig command.
The following location properties are used to enable capture from TDE with AKV -
- SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Vault_URLs
- SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Key_Names
- SqlServer_TDE_AKV_MI_Ids (optional and can be used only with "Managed Identity" authentication)
- SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Tenant_IDs (required for "Service Principal with a Secret" authentication)
- SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Client_Ids (required for "Service Principal with a Secret" authentication)
- SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Client_Secrets (required for "Service Principal with a Secret" authentication)
Examples:
The following examples demonstrate how to add an AKV configuration in HVR using the hvrlocationconfig command. akv1 is the name of this configuration in HVR.
Example 1: Add an AKV configuration with "Managed Identity" authentication
hvrlocationconfig hub_name loc_name "SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Vault_URLs.akv1=https://mykeyvault.vault.azure.net" "SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Key_Names.akv1=MyKey/Version"
If no authentication properties are defined, "Managed Identity" authentication is used by default.
Example 2: Add an AKV configuration with "Managed Identity" authentication using a managed identity client ID:
hvrlocationconfig hub_name loc_name "SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Vault_URLs.akv1=https://mykeyvault.vault.azure.net" "SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Key_Names.akv1=MyKey/Version" "SqlServer_TDE_AKV_MI_Ids=9a4f0022-5143-47fe-be71-beb60b6700d3"
Example 3: Add an AKV configuration with "Service Principal with a Secret" authentication:
hvrlocationconfig hub_name loc_name "SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Vault_URLs.akv1=https://mykeyvault.vault.azure.net" "SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Key_Names.akv1=MyKey/Version" "SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Tenant_IDs.akv1=9a4f0022-5143-47fe-be71-beb60b6700d3" "SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Client_Ids.akv1=a3cd8a22bdb67ceb98c7e6b326b560aa" "SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Client_Secrets.akv1=mysecret"
Instructions for REST API
To add an AKV configuration, use the REST API endpoint for modifying location properties.
The following location properties are used to enable capture from TDE with AKV -
- SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Vault_URLs
- SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Key_Names
- SqlServer_TDE_AKV_MI_Ids (optional and can be used only with "Managed Identity" authentication)
- SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Tenant_IDs (required for "Service Principal with a Secret" authentication)
- SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Client_Ids (required for "Service Principal with a Secret" authentication)
- SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Client_Secrets (required for "Service Principal with a Secret" authentication)
For example, the following request body adds an AKV configuration named akv1 in HVR.
{ "loc_prop_args": [ { "key": ["SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Vault_URLs", "akv1"], "value": "https://mykeyvault.vault.azure.net" }, { "key": ["SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Key_Names", "akv1"], "value": "MyKey/Version" }, { "key": ["SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Tenant_IDs", "akv1"], "value": "9a4f0022-5143-47fe-be71-beb60b6700d3" }, { "key": ["SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Client_Ids", "akv1"], "value": "a3cd8a22bdb67ceb98c7e6b326b560aa" }, { "key": ["SqlServer_TDE_AKV_Client_Secrets", "akv1"], "value": "mysecret" } ] }